Inspiration the SUT faculty member change their mindset about using English language in Thailand classroom. [UKPSF:A1,A3,K2,K5]
ผลการค้นหา: 128
ฟิสิกส์2: กลุ่ม 1
ตารางเรียน :วันจันทร์: 10-12 และ วันพุธ: 10-12 / 17-19
หัวข้อ (สำหรับสอบกลางภาค)
- ทบทวนคณิตศาสตร์ อาทิ เวกเตอร์, แคลคูลัส
- ไฟฟ้าสถิต สนามไฟฟ้า และความจุไฟฟ้า
- พลังงานศักย์ไฟฟ้า และความจุไฟฟ้า
- กระแสไฟฟ้าและวงจรไฟฟ้ากระแสตรง
- สนามแม่เหล็ก กฎของบิโอต์ ซาวารต์ กฎของแอมแปร์
**** VDO การสอน : แจ้ง Link ทาง Facebook และ E learning) ****
This course provides essential principles of hyperspectral remote sensing system and its applications. Also, public and commercial image processing softwares are introduced and applied on hyperspectral image classification along with individual assignment/presentation. Specific topics include (1) principles of hyperspectral remote sensing, (2) data collection and spectral library construction, (3) hyperspectral image preprocessing, (4) hyperspectral image classification algorithms, (5) hyperspectral image classification and accuracy assessment.
Expected learning outcomes
Upon completion of this course, the students should be able to:
1. Explain principles of hyperspectral remote sensing and its applications.
2. Apply image processing softwares for spectral library construction, hyperspectral image preprocessing, image classification and accuracy assessment.
3. Integrate yielded knowledge on hyperspectral remote sensing in practice.
109703 Protein Structure and Engineering 4(4-0-8)
Prerequisite : 109700 Graduate Biochemistry /Consent of the School
Basic review of the structures and properties of amino acid peptide bonds, peptides, polypeptides & proteins, concepts for protein engineering, protein detection, purification and evaluation, electrophoresis, size determination, quaternary structure evaluation, protein primary structure determination, electronic structures and properties of amino acid residues and their reactivities, chemical synthesis of peptides & proteins; biological nucleic acid and protein synthesis & posttranslational modifications, Methods in genetic engineering of proteins, molecular evolution and the use of protein sequence alignment & analysis, physical basis of size and shape determination (e.g. diffusion, analytical centrifugation, light scattering, small angle X-ray scattering), spectroscopic evaluation of secondary structure and tertiary structure, protein structure determination by X-ray crystallography, NMR, & EM tomography, structural modeling and prediction, protein folding, protein interactions with ligands, proteins in membranes, student proposal on protein engineering.
Expected Learning Outcomes
On completion of this course, students are able to
- explain principles of protein structure and the physical interactions involved in attaining protein structure
- understand the basics of the methods and experiments used to study proten structure and structure-function relationships
- evaluate and analyze scientific papers on protein structure and engineering and evaluate the quality of the data
- have a basic understanding of the methods used to engineer proteins and to evaluate the effects of such engineering
- have conscientious in their academic and professional conduct, and able to work with others
- communicate scientific knowledge appropriately and effectively
- Students are eager for knowledge and learning

ศึกษาหลักการการควบคุมการเคลื่อนไหวและการเรียนรู้ทักษะการเคลื่อนไหว การพัฒนาทักษะการเคลื่อนไหว ปัจจัยที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการควบคุมการเคลื่อนไหวและการเรียนรู้ทักษะการเคลื่อนไหว
กิจกรรมแลกเปลี่ยนเรียนรู้ด้านการสอน ในหัวข้อ การพัฒนาการเรียนการสอนรายวิชาโครงงาน โดยใช้วิธีการ “เรียนรู้จากประสบการณ์ประดิษฐ์ (Learning Through Maker Experience)”
โดย ผศ. ดร.บุญส่ง สุตะพันธ์ อาจารย์ประจำสาขาวิชาวิศวกรรมอิเล็กทรอนิกส์ สำนักวิชาวิศวกรรมศาสตร์
พนักงานดีเด่นสายวิชาการ ประจำปี พ.ศ. 2560 ด้านการสอน กลุ่มผู้มีประสบการณ์การสอนในสถาบันอุดมศึกษาตั้งแต่ 3 - 10 ปี
ในวันอังคารที่ 17 กรกฎาคม 2561 ตั้งแต่เวลา 13.30 น. เป็นต้นไป ณ ห้องประชุม 1 ชั้น 1 อาคารวิชาการ 1
Course Description
trends, theories, research, and controversial issues in different areas of English language studies such as educational reform, corpus linguistics, second language acquisition, computer-assisted language learning, teaching methodology, assessment, syllabus design, discourse analysis, etc. are discussed. Related on-line databases are also introduced to students.
Course Coordinators: Assoc. Prof. Songphorn Tajaroensuk
Developing students’ abilities for effective communication in social settings; focusing on integrated skills with the primary emphasis on listening and speaking; developing communication and language learning strategies; and promoting autonomous learning using various resources
Enhancing students’ proficiency in social communication; developing students’ ability to accomplish learning tasks; using integrated skills and task-based learning with emphasis on contemporary themes and current issues; reading semi-academic texts from a variety of authentic sources such as newspapers, magazines and online resources
เพิ่มพูนทักษะภาษาอังกฤษเพื่อการสื่อสารในระดับที่สูงขึ้น พัฒนาทักษะทางภาษาและกลวิธีในการเรียนรู้ภาษา บูรณาการทักษะทางภาษาและส่งเสริมให้ทำกิจกรรมแบบเผชิญประสบการณ์ เน้น เนื้อหาในหัวข้อเรื่อง และประเด็นร่วมสมัยกึ่งวิชาการจากแหล่งข้อมูลต่าง ๆ โดยไม่มีการดัดแปลงภาษา เช่น หนังสือพิมพ์ บทความในนิตยสาร และแหล่งข้อมูลอิเลคทรอนิคส์
ความหมายและความสําคัญของความรู้ ประเภทและระดับของความรู้ รูปแบบการคิดและการเรียนรู้ของมนุษย์ กรอบแนวคิดการจัดการความรู้ องค์ประกอบของการจัดการความรู้ กระบวนการของการจัดการความรู้ การสร้างความรู้ ระบบการจัดเก็บและค้นคืนองค์ความรู้การจัดการความรู้ในภาคต่าง ๆ เช่น ภาคธุรกิจ ภาครัฐ ภาคการศึกษา เป็นต้น
Definition and importance of knowledge; types and levels of knowledge; human thinking patterns and human learning processes; knowledge management frameworks; components of knowledge management; knowledge management process; knowledge creation; knowledge storage and retrieval systems; knowledge management in business, government, education sectors, etc.
This research-driven course will focus on developing innovation and creativity as catalysts for new research into new theoretical models as well as techniques for improving learning opportunities in both institutional and non-institutional settings. To this end, it will encourage students to review current educational contexts, question current dominant models of (language) learning/teaching, identify and examine new ones and develop their own. Importantly, it will draw on interdisciplinary areas such as brain research and perception and awareness studies as well as modern intellectual directions such as critical theory and postmodern thought to guide its development. It will also draw on the great potential of modern technology both to support learning/teaching and to investigate it (especially through its potential to offer new ways of thinking about language education

245302 การพัฒนาภาวะผู้นำ 2(1-2-3)
(Leadership Development)
วิชาบังคับก่อน : ไม่มี
แนวคิดภาวะผู้นำ คุณลักษณะและบทบาทของผู้นำ การประเมินภาวะผู้นำของตนเอง เทคนิคการพัฒนาตนเอง การพัฒนาทักษะระหว่างบุคคล การพัฒนาทักษะในการพัฒนางาน เน้นการฝึกปฏิบัติ กิจกรรมฝึกฝนตนเองและกิจกรรมกลุ่ม
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ที่คาดหวังระดับรายวิชา
นักศึกษาที่ผ่านรายวิชานี้มีความสามารถ ดังนี้
1. อธิบายแนวคิดภาวะผู้นำ คุณลักษณะและบทบาทของผู้นำ
2. ประเมินภาวะผู้นำของตนเอง
3. ฝึกปฏิบัติกิจกรรมฝึกฝนตนเองและกิจกรรมกลุ่ม
4. พัฒนาทักษะระหว่างบุคคลและเทคนิคการพัฒนาตนเอง
245302 Leadership Development 2(1-2-3)
Pre-requisite : None
Strategic leadership concept, characteristics and roles of leaders, leadership self-assessment, self-development techniques, interpersonal skills development, task skills development emphasizing practices, self-development activities and team activities
Course learning outcomes
Having successfully completed this course, student must be able to:
1. Explain strategic leadership concept, characteristics and roles of leaders
2. Evaluate self-leadership
3. Practice activities in forms of self-training and team-training
4. Develop interpersonal skills and self-development techniques
Plant Breeding is an undergrad course that requires the use of e-learning 2 system for distributing class materials and feedback
.
รหัสและชื่อรายวิชา
802313 การจัดการมูลฝอย
802313 Solid Waste Management
รายวิชาที่ต้องเรียนมาก่อน (Pre-requisite) / รายวิชาที่ต้องเรียนพร้อมกัน (Co-requisites)
802302 พื้นฐานการออกแบบงานอนามัยสิ่งแวดล้อม หรือโดยความเห็นชอบของสาขาวิชา
คำอธิบายรายวิชา (Course Description)
หลักการจัดการมูลฝอยชุมชน มูลฝอยติดเชื้อ มูลฝอยที่เป็นพิษหรืออันตรายจากชุมชน และสิ่งปฏิกูล แหล่งกำเนิด องค์ประกอบ ลักษณะสมบัติ และการเก็บตัวอย่างและตรวจวิเคราะห์ทางห้องปฏิบัติการ การประมาณอัตราการเกิดจากแหล่งกำเนิดต่างๆ ในชุมชนทั้งจากครัวเรือน สถานบริการ และโรงงานอุตสาหกรรม การเก็บรวบรวม การคัดแยก การขนถ่าย และการเก็บขน เทคโนโลยีและการจัดการในการบำบัดและกำจัด การวางแผนและการลดปริมาณ การนำกลับมาใช้ซ้ำ และการนำกลับมาใช้ใหม่ รวมถึงกฎหมายที่เกี่ยวข้อง
ภาคการศึกษา / ผู้เรียน / สถานที่เรียน
ภาคการศึกษาที่ 3/2566
ผู้เรียน: นักศึกษาสาขาวิชาอนามัยสิ่งแวดล้อม ชั้นปีที่ 3 จำนวนผู้เรียนที่รับได้ ประมาณ 90 คน
สถานที่เรียนและเวลา: อาคารปฏิบัติการด้านเทคโนโลยีดิจิทัล (B6) ห้อง B6110-A วันพฤหัสบดี เวลา 13.00-17.00 น. กลุ่ม1
ENG35 4505 Reverse Engineering 2(1-3-5)
Prerequisite : none Course Type: Technical Elective
This course Introduces learners to Reverse Engineering (RE). Applying RE
methodologies allow learners to test and analyse an object or a system in order to; identify,
understand, and document its functionality and operation. RE can play a key role in helping
learners understand engineering products to develop a better device.
Learning outcomes
1. Ability to explain reverse engineering concept.
2. Ability to use information requirements and factors influencing to apply with reverse engineering.
3. Ability to use reverse engineering concept for designs with satisfy functional and legal requirements.
Course Learning Outcomes:
- To apply computer programming in calculation and solving the problems related to chemical engineering, especially by numerical methods both by spreadsheet program and computer language.
- To appropriately apply digital technology for necessary information and numerical methods for problem solving.
- To effectively apply computer programming skills, especially numerical methods, on solving noncomplex chemical engineering problem; for example, on group-assigned term projects.
- To efficiently explain problem solving methods, computer programming and numerical results of group-assigned term projects.
- To understand the importance and method of citation for references, especially on the references that students use in their term projects.
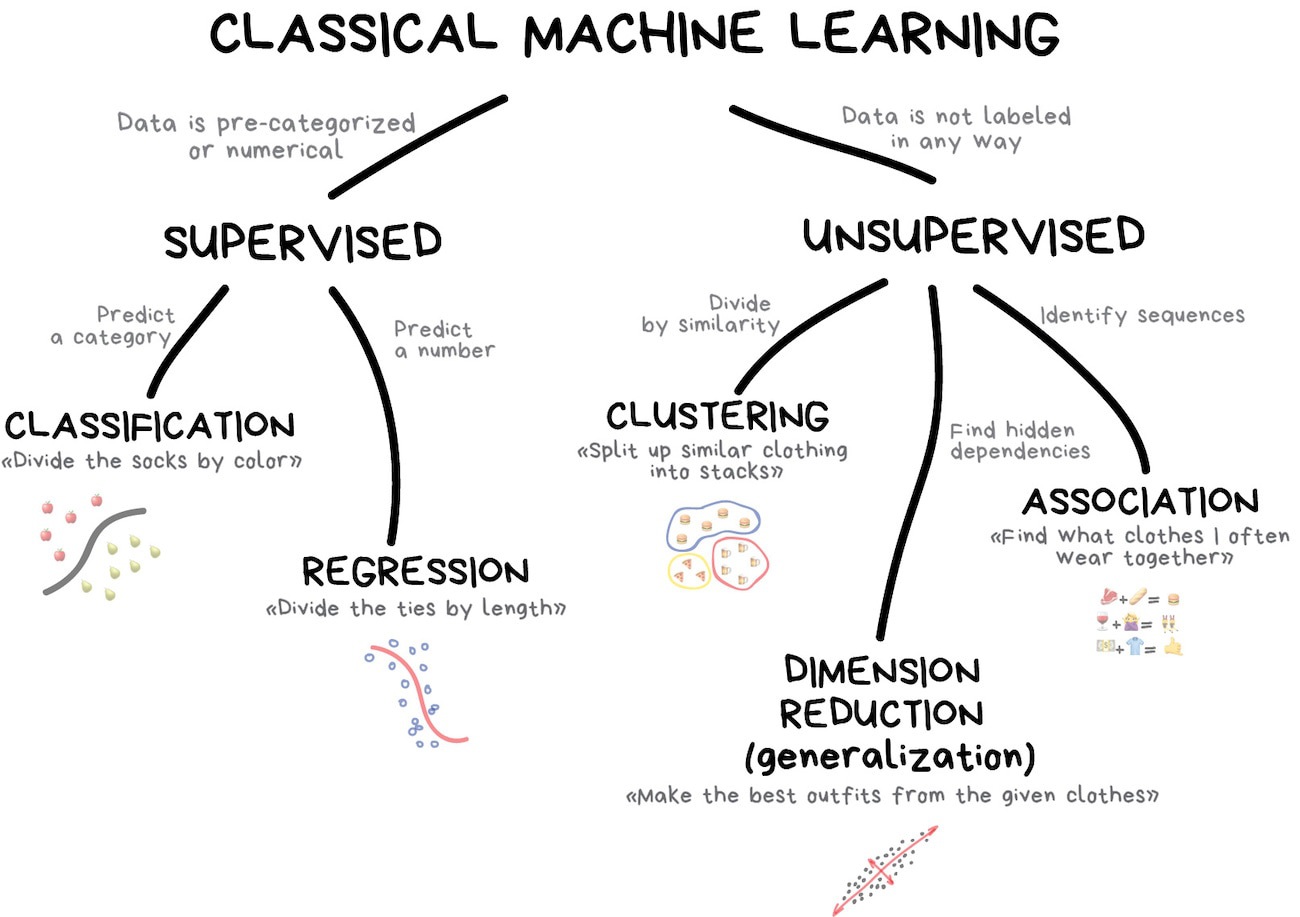
This course provides an introduction of machine learning theory and programming. Topics include (i) programming with libraries related to machine learning (ii) supervised learning (parametric/non-parametric algorithms, support vector machines, kernels, neural networks. (ii) unsupervised learning (k-mean clustering, principle component analysis: PCA). This course will also draw from numerous case studies and applications, so that student will learn how to apply learning algorithms to build smart robots (perception & control), speech recognition, computer vision and other areas.

ระบบควบคุมการขับขี่อัตโนมัติมีการพัฒนาอย่างต่อเนื่องโดยมีการประยุกต์ใช้ Artificial Intelligence อาทิ เรียนรู้ของเครื่อง (Machine Learning) กับยานยนต์ในระบบต่างๆ ไม่ว่าจะเป็นการมองเห็นหรือการรับรู้ แยกแยะสิ่งที่โดยรอบยานยนต์ เพื่อทำให้ยานยนต์สามารถนำข้อมูลต่างๆ เหล่านั้นมาใช้ในการควบคุมให้ยานยนต์สามารถทำภารกิจได้สมบูรณ์ ตัวอย่างเช่น ระบบ Adaptive Cruise Speed Control, Lane Tracking System ใช้การมองเห็นของคอมพิวเตอร์ (Computer Vision) รวมถึงการมองเห็นวัตถุที่กีดขว้างเส้นทาง และใช้เป็นข้อมูลในการตัดสินการสร้างเส้นทางหลบหลีกนั้นเอง

คำอธิบายรายวิชา
หลักการเบื้องต้นของระบบเครื่องมือสำหรับการวัดและระบบควบคุมที่เกี่ยวข้องกับกระบวนการขึ้นรูปพอลิเมอร์ หัวข้อที่รวมอยู่ในวิชานี้ได้แก่ พื้นฐานการวัด หลักการทำงาน และองค์ประกอบของเครื่องมือวัดและระบบควบคุม เซ็นเซอร์ที่ใช้ในงานทางวิศวกรรม ระบบการควบคุมและการปรับตั้งตัวแปรระบบการควบคุมต่างๆ
ผลสัมฤทธิ์การเรียนรู้ (Learning Outcome)
เมื่อสิ้นสุดการเรียนรายวิชานี้ ผู้เรียนควรมีความสามารถด้านต่างๆ ต่อไปนี้
Course Content
ประเภทและการใช้งานวัสดุพอลิเมอร์ วัสดุพอลิเมอร์ในชีวิตประจำวัน/ในงานเชิงวิศวกรรม/ชนิดสมรรถนะสูง/ชนิดพิเศษ กลุ่มการใช้งานวัสดุพอลิเมอร์ การทดสอบสมบัติทางกล ความร้อน ไฟฟ้า แสง เคมี การติดไฟ และการกั้นการแพร่ผ่าน เทอร์โมพลาสติก เทอร์โมเซต อิลาสโตเมอร์ พอลิเมอร์ผสมและ (นาโน) คอมพอสิท พอลิเมอร์ชีวภาพและพอลิเมอร์แตกสลายได้ทางชีวภาพ บล็อกโคพอลิเมอร์ การนำไปใช้ประโยชน์ขั้นสูง
Course Learning Outcomes
เมื่อสิ้นสุดการเรียนรายวิชานี้ ผู้เรียนควรมีความสามารถด้านต่างๆ ต่อไปนี้ สามารถเชื่อมโยงได้ระหว่างโครงสร้างและสมบัติและสมรรถนะของเทอร์โมพลาสติก เทอร์โมเซต และ อิลาสโตเมอร์ สามารถเลือกวัสดุพอลิเมอร์และผลิตภัณฑ์สำหรับการใช้งานที่จำเพาะเจาะจง
Course Responsibility to Program Learning Outcomes (ความรับผิดชอบของรายวิชาต่อผลลัพธ์การเรียนรุ้ของหลักสูตร)
PLO3: สามารถประยุกต์ใช้การออกแบบทางวิศวกรรมพอลิเมอร์เพื่อพัฒนาผลิตภัณฑ์พอลิเมอร์ที่ตรงวัตถุประสงค์การใช้งานและตรงตามความต้องการของผู้บริโภคโดยคำนึงถึง สิ่งแวดล้อม ความปลอดภัย และปัจจัยทางสังคมที่เกี่ยวข้องกับประชาคมโลก
PLO5: สามารถทำงานร่วมกับทีมงานที่มีสมาชิกจากหลายสาขาวิชาชีพ ในฐานะสมาชิกในทีม และมีความเป็นผู้นำ
PLO6: สามารถติดต่อสื่อสารในงานวิศวกรรมได้อย่างมีประสิทธิผลกับผู้รับที่หลากหลาย ทั้งภาษาไทยและภาษาต่างประเทศ ด้วยวาจา การเขียนรายงาน การเสนอผลงาน ทางวิศวกรรมพอลิเมอร์
ปฏิบัติการทดลองเกี่ยวกับเครื่องมือวัดและระบบการควบคุมเครื่องจักรในกระบวนการขึ้นรูปพอลิเมอร์
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ของรายวิชา (Course Learning Outcomes)
CLO1: อธิบายหลักการทำงานเบื้องต้นของเครื่องมือวัดและระบบการควบคุมเครื่องจักรในกระบวนการขึ้นรูปพอลิเมอร์
CLO2: สามารถใช้เครื่องมือวัดและระบบควบคุมได้ถูกต้องเหมาะสม (PI3.1)
CLO3: สามารถเขียนรายงานการทดสอบ โดย
- § สามารถรวบรวมข้อมูลจากการทดลอง ประมวล และนำเสนอข้อมูลที่ได้ในรูปของกราฟหรือตารางอย่างเหมาะสม
- § สามารถคำนวณค่าต่างๆ โดยใช้สมการที่เกี่ยวข้องได้อย่างถูกต้อง
CLO4: สามารถใช้หลักการพื้นฐานทางวิทยาศาสตร์และวิศวกรรมศาสตร์ของพอลิเมอร์ในการอภิปรายผลการทดลองและสรุปผลการทำปฏิบัติการ
CLO5: นำเสนอผลการทดสอบ ในรูปแบบตารางหรือกราฟ
CLO6: สามารถประสานงานในทีมจนทำให้งานสำเร็จ
ความรับผิดชอบของรายวิชาต่อผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ของหลักสูตร (Program Learning Outcomes)
PLO3: สามารถพัฒนาและดำเนินการตรวจสอบและทดสอบ ทดลองที่เหมาะสม วิเคราะห์และแปรผลข้อมูล โดยใช้วิจารณญาณทางวิศวกรรมพอลิเมอร์ เพื่อสรุปผลการทดลอง
PLO5: สามารถทำงานร่วมกับทีมงาน อย่างมีประสิทธิผล ฐานะสมาชิกในทีม มีความเป็นผู้นำ สร้างการมีส่วนร่วมและบรรยากาศการทำงานร่วมกัน กำหนดเป้าหมาย แผนงาน จนทำให้งานสำเร็จ
PLO7: สามารถแสวงหาและประยุกต์ใช้ความรู้ใหม่ ตามต้องการได้ ด้วยการใช้กลยุทธิ์การเรียนรู้ที่เหมาะสม

528403 Safety Engineering
Principles of health, safety and environmental protection, mechanical hazards and safeguarding, electrical hazards and safety, fire and explosion hazards and protection, toxic substances and explosive hazards and safety, heat and temperature hazards at work, safety laws, principle of safety management , element of industrial safety psychology.
Learning Outcomes
On completion of this course, the student should be able to
- Analysis the causes of accidents and hazards that can occur in workplaces,
- Properly selects safeguarding and protective equipment for different work environments.
- Identify the common injuries and correctly provide fist aids to the injured person.
- Become aware of the safety of oneself, collogues, and environment.
Couse Description
This course will cover the fundamentals of engineering design for plastic injection mold, mold cost estimation, and basic product design for injection molding manufacturing. Topics include mold type, structure, and standard components and theirs functions, design of balanced runners, design of gates, vents, cooling, and ejecting system, estimate mold shrinkage, mold material selection and maintenance.
Learning Outcomes
On completion of this course, the student should be able to
1. Explain the mold manufacturing process.
2. Identify classifications of molds, the considerations necessary for design, and the function of design components.
3. Estimate cost of plastic products, molds, and time for mold manufacturing
4. Design a system, component, or process to meet desired needs
5. Apply knowledge of mathematics, science, and engineering to analyze and solve engineering problem.

ชื่อวิชา วิศวกรรมความปลอดภัย
คำอธิบายรายวิชา
หลักการเกี่ยวกับชีวอนามัย ความปลอดภัย และการป้องกันเชิงสิ่งแวดล้อม อันตรายจากเครื่องจักรกลและอุปกรณ์ป้องกัน อันตรายจากไฟฟ้าและอุปกรณ์ป้องกัน อันตรายจากอัคคีภัย การประทุ และวิธีป้องกัน ความปลอดภัยจากสารเคมีเป็นพิษและประทุได้ อันตรายจากความร้อนและการทำงานที่อุณหภูมิสูง กฎหมายเกี่ยวกับความปลอดภัย หลักการจัดการเรื่องความปลอดภัยในการทำงาน สาระสำคัญเกี่ยวกับความปลอดภัยและหลักจิตวิทยาในอุตสาหกรรม
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ของหลักสูตรที่รายวิชารับผิดชอบ
PLO1: สามารถระบุประเด็นปัญหา หาแนวทางแก้ปัญหาทางวิศวกรรมพอลิเมอร์ที่ซับซ้อนได้ โดยประยุกต์หลักการทางด้านวิศวกรรมศาสตร์ วิทยาศาสตร์ และคณิตศาสตร์
PLO6: มีความเข้าใจความรับผิดชอบของวิศวกรตามกรอบมาตรฐานการปฏิบัติวิชาชีพและจรรยาบรรณแห่งวิชาชีพวิศวกรรมพอลิเมอร์ มีวิจารณญาณ การพิจารณาตัดสินใจ ที่ต้องคำนึงถึงผลกระทบต่อโลกเศรษฐกิจ-สังคม และสิ่งแวดล้อม
Course Description
Principles of health, safety and environmental protection, mechanical hazards and safeguarding, electrical hazards and safety, fire and explosion hazards and protection, toxic substances and explosive hazards and safety, heat and temperature hazards at work, safety laws, principle of safety management, element of industrial safety psychology.
Course Responsibility to Program Learning Outcome
PLO1: An ability to identify, formulate, and solve complex polymer engineering problems by applying principles of engineering science, and mathematics.
PLO6: An ability to recognize ethical and professional responsibilities in polymer engineering situations and make informed judgement, which must consider the impact of polymer engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts.

This online course is for the 530211 and 582211 students to have chances to practices their online midterm examination and to let them get use to with the SUT E-learning system. After practicing the examinations, they will have knowledge and skills to do their incoming examinations effectively.

Learning about Software or Information Technology that most used in Industrial Engineer and Practice to write computer programming for Industrial Engineer
Try to use e-learning and e-test system
Aims and Summary
This course aims to provide basic knowledge about polymeric biomaterials, physico-chemical properties of biomaterials, host reactions to biomaterials and their evaluation, biological testing of biomaterials and degradation of materials in biological environment, inform about current issues in biomaterials, hand-on mini-project on fabrication and characterization of a simple polymeric biomaterial. Develop entrepreneurial mindset for polymeric biomaterials.
Teaching and Learning:
This module has been designed to align with the following PLO
PLO3: Analyze materials engineering problem, design and conduct experiment, analyze the obtained data, and explain results to the desired outcome.
Module Learning Outcomes
MLO1 describe basic definition of biomaterials, classify biomaterials according to the structural properties
MLO2 identify the properties required to meet the needs of the intended biological function and describe host reactions to biomaterials
MLO3 Select material to meet requirements for a specific application or design
MLO4 Independently search and review articles related to current issues in biomaterials, write a scientific report and present to the class.
MLO5 Fabricate simple biomaterial samples and evaluate their properties by perform a series of test and characterization
MLO6 Develop a business plan for a biomaterial product (Not Applicable)
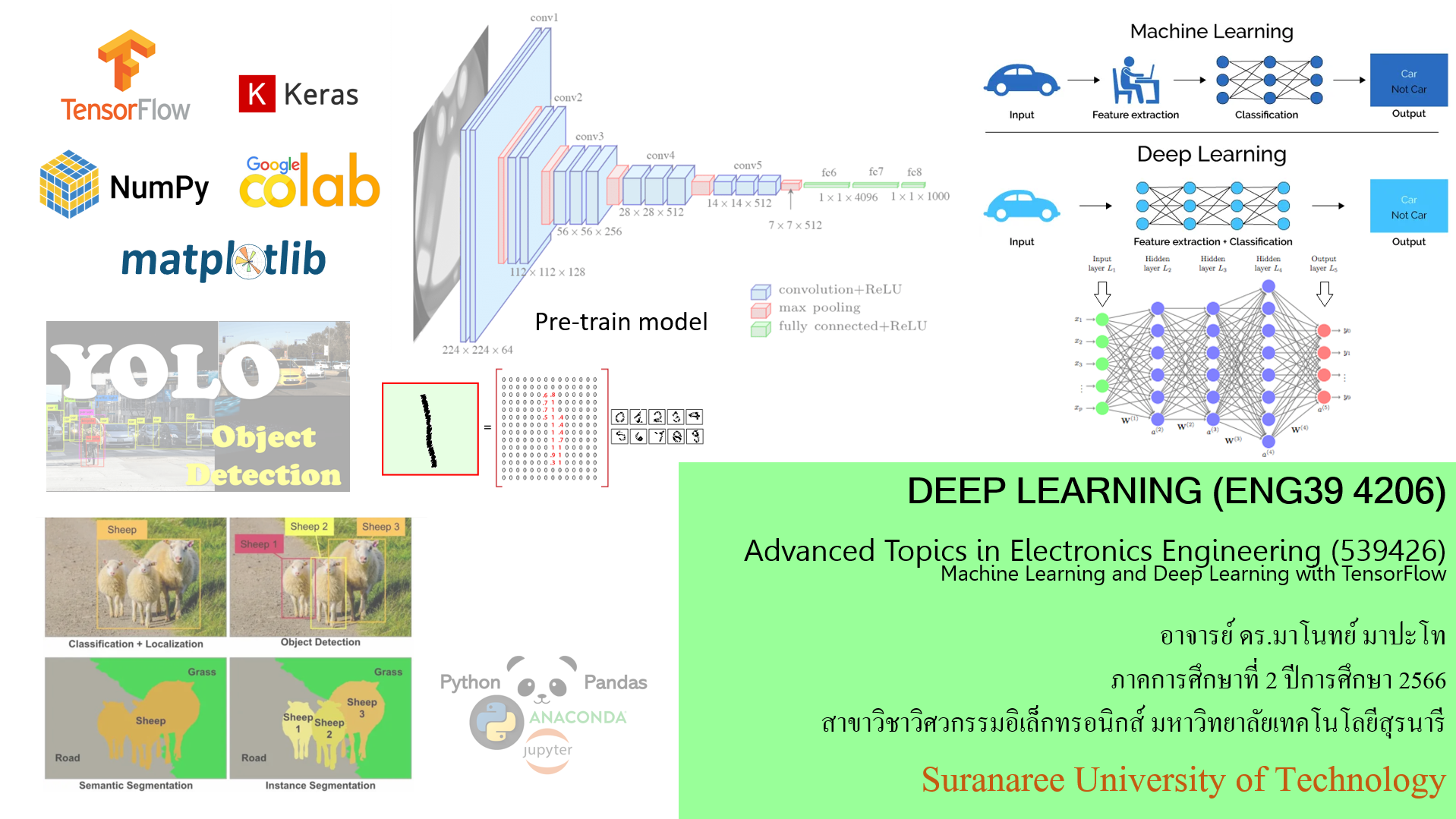
- Machine learning and introduction to deep Learning I
- Machine learning and introduction to deep Learning II
- Deep learning for machine visions I
- Deep learning for machine visions II
- Deep learning deployment projects


Course Outline
Structure and properties of ceramic materials; Conventional and advanced ceramic; Ceramic processing and engineering applications of ceramics; Polymer as an engineering material, Polymer blends, Polymer composites, Chain structure of polymers, Mechanical and thermal properties of polymers, Polymerization, Polymer processing, Polymer degradations; Polymeric and Ceramic Materials for engineering application.
Course Learning outcomes
CLO1: Students are able to describe basic properties of polymeric and ceramic materials.
CLO2: Students are able to relate structure and properties of polymeric and ceramic materials.
CLO3: Students are able to explain the materials processing techniques.
CLO4: Students are capable of select appropriate materials for the desired basic engineering applications.
Structure and properties of ceramic materials; Conventional and advanced ceramic; Ceramic processing and engineering applications of ceramics; Polymer as an engineering material, Polymer blends, Polymer composites, Chain structure of polymers, Mechanical and thermal properties of polymers, Polymerization, Polymer processing, Polymer degradations; Polymeric and Ceramic Materials for engineering applications.
Learning outcomes
- Students are able to describe basic properties of polymeric and ceramic materials.
- Students are able to relate structure and properties of polymeric and ceramic materials.
- Students are able to explain the materials processing techniques.
- Students are capable of select appropriate materials for the desired basic engineering applications.
This course is for student who had enrolled, attended lectures and took all the exams, but failed, 583305 in 1/2023. As a result, there will not be regular lectures but there will be online assignments and feedback provision throughout this trimester.
Course evaluation
1. Assignments via SUT e-learning (20%)
2. 3 Exams
- Exam 1 : Saturday 16 December 2023 9.00 am 12.00 (noon) (25%)
- Exam 2 : Saturday 13 January 2024 9.00 am 12.00 (noon) (25%)
- Exam 3 : Saturday 3 February 2024 9.00 am 12.00 (noon) (30%)
585310 Computer Aided Engineering I 2 (1-3-5)
Prerequisites : 585202 Mechanical Engineering Mathematics II and 585303 Machine Design
Course Description :
Use of computer for design and analysis of mechanical engineering problems. Physical modeling and simulations of mechanical engineering problems and related applications. Specifications of boundary conditions and initial conditions, verification of simulated results.
Learning outcomes :
Student will be able to create physical models which correspond to engineering problems. Student will be able to identify errors that may occur in simulations. Student will be able to use computer to design and analyze engineering problems correctly.
585340 Mechanical Engineering Laboratory I 1(0-3-3)
Prerequisites : 582211 Mechanics of Materials 585204, Thermodynamics I and 585207 Fluid Mechanics
Course Discription :
Experiments in instrumentation and measurement for mechanical engineers such as pressure, fluid flow, temperature, displacement, force, and strain; experiments in material testing, fluid mechanics, and thermodynamics, interpretation of experimental data,technical report writing.
Learning outcomes :
After the course, the students should be able to:
- Select and use appropriate measuring devices and techniques commonly used in mechanical engineering systems.
- Conduct experiments in material testing, fluid mechanics, and thermodynamics, as well as analyze and interpret data.
- Demonstrate technical writing skills.
- Develop work habits those are necessary for effective collaboration with other students.


585401 Computer Aided Engineering II 2(1-3-5)
Prerequisite : 585310 Computer Aided Engineering I,
Use of computer for design and analysis of mechanical engineering problems. Physical modeling and simulations of mechanical engineering problems and related applications, project based on using computer for design and analysis of related mechanical engineering problems.
Learning outcomes
Student will be able to create specific physical model for mechanical engineering problems. Student will be able to simulate and analyze mechanical engineering problems using commercial software. Student will be able to analyze accuracy of simulation applied for solving problems. Student will be able to apply computer aided engineering to conduct related mechanical engineering projects.

แนะนำเกี่ยวกับกระบวนการวัดและหน่วยวัด การวิเคราะห์แรงที่กระทำกับโครงสร้างทางวิศวกรรมในสภาวะสมดุล คุณสมบัติของแรง โมดมนต์ คู่ควบ และผลลัพธ์ของระบบแรง สภาวะสมดุล แรงเสียดทาน เซนทรอยด์ โมเมนต์ความเฉื่อยของพื้นที่ พื้นฐานของกลศาสตร์นิวโทเนียนซึ่งครอบคลุมถึงจลนศาสตร์ และจลนพลศาสตร์ การเคลื่อนที่ที่สัมพันธ์กับตำแหน่งอ้างอิงที่เคลื่อนที่ งานและพลังงาน แรงกระตุ้นและโมเมนตัม พลศาสตร์ของวัสดุแข็งเกร็ง แนะนำเกี่ยวกับการเคลื่อนที่ของวัตถุแข็งเกร็งในระนาบ
Introduction to measurement and unit. Analysis of forces on engineering structures in equilibrium. Properties of forces, moments, couples, and resultants. Equilibrium conditions, friction, centroids, area moments of inertia. Fundamentals of Newtonian mechanics, including kinematics and kinetics, motion relative to moving reference frames, work and energy, impulse and momentum, rigid body dynamics. Introduction to plane motion of rigid bodies.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. ระบุหน่วยของปริมาณพื้นฐานที่เกี่ยวข้องกับปัญหาทางวิศวกรรม
Identify units of basic quantity related to engineering problems.
CLO2. วาดฟรีบอดี้ไดอะแกรมสำหรับวัตถุแข็งเกร็ง โครงกรอบและเครื่องจักรล และสร้างสมการสภาวะสมดุลสำหรับไดอะแกรมนั้น
Draw Free Body Diagrams (FBD) for rigid bodies, frames and machines, and set up equilibrium equations (i.e. forces and couples) for them.
CLO3. นำทฤษฏีที่เกี่ยวข้องกับกลศาสตร์ของแข็งไปใช้เพื่อคำนวณแรง ระยะโก่ง โมเมนต์ ความเค้น และความเครียด
Apply the formal theory of solid mechanics to calculate forces, deflections, moments stress and strain.
CLO4. วิเคราะห์ผลกระบทบของระบบแบ่งแรงซึ่งประกอบด้วยการคำนวณเซนทรอยด์และโมเมนต์ความเฉื่อย
Analyze the effect of distributed force systems including the calculation of centroids and moments of inertia.
CLO5. วิเคราะห์ความสัมพันธ์ของจลนศาสตร์ซึ่งประกอบด้วยการคำนวณความเร็วและความเร่งของอนุภาค
Analyze kinematics relations including the calculation of velocity and acceleration of particles.
CLO6. นำทฤษฎีความสัมพันธ์ของความเร็วและความเร่งไปใช้แก้ปัญหาจลนศาสตร์ของอนุภาค
Utilize the relative velocity and acceleration expression to solve kinematics problems of particles.
CLO7. วิเคราะห์ความสัมพันธ์ของจลนศาสตร์ซึ่งประกอบด้วยการคำนวณความเร็วและความเร่งของอนุภาค
Analyze kinetics relations including the calculation of velocity and acceleration of particles.
CLO8. เลือกสมการพื้นฐานของกลศาสตร์เพื่อแก้ปัญหาด้านต่างๆ เช่น การอนุรักษ์พลังงาน การอนุรักษ์โมเมนตัม กฎข้อที่ 2 ของนิวตัน เป็นต้น
Choose carefully among different fundamental equations of dynamics to solve problems such as conservation of energy, conservation of momentum, or Newton’s 2nd law.
CLO9. อธิบายการเคลื่อนที่ของวัตถุแข็งเกร็งในระนาบ
Describe the plane motion of rigid bodies.
ENG35 2011 แนะนำวิศวกรรมการผลิต 1(0-3-3)
(Orientation to Manufacturing Engineering)
วิชาบังคับก่อน : ไม่มี
เตรียมพื้นฐานของผู้ศึกษาด้านวิศวกรรมการผลิต ศึกษาภาพรวมของหลักสูตรและภาพรวมของการประกอบวิชาชีพ อธิบายผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ที่คาดหวังของหลักสูตร ศึกษาอุปกรณ์ เครื่องมือ และโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์เบื้องต้นเพื่อช่วยในเรียนรู้ การเขียนรายงาน การนำเสนองานทางวิศวกรรม ความสำคัญของระบบอัตโนมัติอุตสาหกรรมและอุปกรณ์พื้นฐานของระบบอัตโนมัติอุตสาหกรรม เช่น เซนเซอร์ ระบบกระตุ้น มอเตอร์ ระบบอัตโนมัตินิวเมติกส์ ระบบไฮดรอลิกส์
ผลสัมฤทธิ์การเรียนรู้
1. สามารถอธิบายความสำคัญและบทบาทของวิศวกรรมการผลิตได้
2. รับผิดชอบต่องานที่ได้รับมอบหมาย
ENG35 2011 Orientation to Manufacturing Engineering 1(0-3-3)
Prerequisite : none
Basic requirements in studying manufacturing engineering; overview of the program and prospective careers; explain expected learning outcomes; learn equipment, tools, and basic computer software for aiding the study; report writing and presentation, Importance of industrial automation system; basic equipment for industrial automation such as sensors, actuators, motors, pneumatics, and hydraulics.
Learning outcomes
1. Ability to explain knowledge of significances and responsibilities of manufacturing engineer.
2. Ability to be responsible for engineering practice.
กระบวนการออกแบบ และเครื่องมือทางด้านกราฟฟิคสำหรับการสื่อสารเบื้องต้นที่ใช้โดยวิศวกร การบันทึกเอกสารของการออกแบบโดยการวาดด้วยมือ และการวาดเชิงวิศวกรรม หลักการพื้นฐานของเรขาคณิตเชิงพรรณนา การใช้เครื่องมือทางคอมพิวเตอร์ช่วยในการออกแบบ หลักการเบื้องต้นของการออกแบบเพื่อกระบวนการผลิต เน้นการทำงานเป็นกลุ่ม และการวิจารณ์โดยเพื่อร่วมกลุ่มสำหรับการผลิตชิ้นส่วนเพื่อการประกอบ โครงงานการออกแบบแนวความคิดที่นำเสนอผ่านแบบทางวิศวกรรม และการทำปฏิบัติการผ่านเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์
Introduction to the design process and graphical communications tools used by engineers. Documentation of design through freehand sketching and engineering drawings. Basic descriptive geometry. Computer-aided design as a design tool. Introduction to design for manufacturability. Emphasis of group work and peer review in the production of part for assemblies. Conceptual design projects presented in technical drawing format. Computer Laboratory.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. อ่านและอธิบายแบบวิศวกรรม และแสดงให้เห็นถึงความสามารถในการใช้งานคำศัพท์และสัญลักษณ์ในการสื่อสารเชิงวิศวกรรม
Read and interpret engineering drawings. Demonstrate the use of terminology and symbols used in engineering communications.
CLO2. เขียนแบบทางวิศวกรรม และสร้างเอกสารที่ใช้ในการสื่อสารซึ่งประกอบด้วยการอธิบายอุปกรณ์เชิงกล และระบบผ่านจุด เวกเตอร์ และพื้นผิว
Create engineering drawings. Construct engineering communication documents describing mechanical devices and systems by using points, vectors, and surfaces.
CLO3. เลือกใช้ภาพฉายสองมิติ ภาพตัด ภาพช่วย และภาพสามมิติเพื่อสื่อสารแนวคิดของแบบทางวิศวกรรมให้กับผู้ผลิดได้อย่างเหมาะสม
Select appropriate orthographic, sectional, auxiliary, and pictorial views, to convey engineering design concepts to fabricators.
CLO4. กำหนดมิติ และความคลาดเคลื่อนทางเลขาคณิตเพื่อสื่อสารข้อกำหนดการออกแบบการทำงานของชิ้นส่วนได้อย่างเหมาะสม
Construct appropriate dimensions and geometric tolerances to convey a part’s functional design requirements to fabricators
CLO5. คำนวณความคลาดเคลื่อนของขนาดที่จำเป็นเพื่อรับรองความสัมพันธ์ของการทำงานกับการประกอบชิ้นส่วนหลายชิ้นส่วนเข้าด้วยกัน
Calculate size tolerances necessary to ensure the functional relationship to multi-part assemblies.
CLO6. สร้างและกำหนดแนวคิดวิธีแก้ไขปัญหาทางวิศวกรรม
Create and define a conceptual solution to an engineering problem.
CLO7. ใช้โปรแกรมสำเร็จรูปช่วยการออกแบบเพื่อสร้างเอกสารแบบทางวิศวกรรม
Use a common industrial CAD package to create engineering documentation.
ENG35 2011 แนะนำวิศวกรรมการผลิต 1(0-3-3)
(Orientation to Manufacturing Engineering)
วิชาบังคับก่อน : ไม่มี
เตรียมพื้นฐานของผู้ศึกษาด้านวิศวกรรมการผลิต ศึกษาภาพรวมของหลักสูตรและภาพรวมของการประกอบวิชาชีพ อธิบายผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ที่คาดหวังของหลักสูตร ศึกษาอุปกรณ์ เครื่องมือ และโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์เบื้องต้นเพื่อช่วยในเรียนรู้ การเขียนรายงาน การนำเสนองานทางวิศวกรรม ความสำคัญของระบบอัตโนมัติอุตสาหกรรมและอุปกรณ์พื้นฐานของระบบอัตโนมัติอุตสาหกรรม เช่น เซนเซอร์ ระบบกระตุ้น มอเตอร์ ระบบอัตโนมัตินิวเมติกส์ ระบบไฮดรอลิกส์
ผลสัมฤทธิ์การเรียนรู้
1. สามารถอธิบายความสำคัญและบทบาทของวิศวกรรมการผลิตได้
2. รับผิดชอบต่องานที่ได้รับมอบหมาย
ENG35 2011 Orientation to Manufacturing Engineering 1(0-3-3)
Prerequisite : none
Basic requirements in studying manufacturing engineering; overview of the program and prospective careers; explain expected learning outcomes; learn equipment, tools, and basic computer software for aiding the study; report writing and presentation, Importance of industrial automation system; basic equipment for industrial automation such as sensors, actuators, motors, pneumatics, and hydraulics.
Learning outcomes
1. Ability to explain knowledge of significances and responsibilities of manufacturing engineer.
2. Ability to be responsible for engineering practice.
Description:
ฝึกปฏิบัติการคำนวณปัญหาทางวิศวกรรมและสร้างแผนภาพนำเสนอข้อมูลโดยใช้ฟังก์ชั่นของโปรแกรมประยุกต์พื้นฐาน การเขียนมาโคร การเขียนโปรแกรมด้วยวิชวลเบสิคเพื่อควบคุมโปรแกรมประยุกต์พื้นฐาน
Practice in computing engineering problems and creating a chart for presentation using features, Macro, and program with Visual Basic for Applications in spreadsheet software.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. ใช้โปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์ประเภทตารางคำนวณมาแก้ปัญหาทางวิศวกรรมพื้นฐานได้ รวมถึงการนำเสนอข้อมูลด้วยแผนภูมิได้
Ability to apply computer application such as spreadsheet for modelling and solving basic engineering problems, and creating diagram presentation of data.
Introduction to the design process and graphical communications tools used by engineers. Documentation of design through freehand sketching and engineering drawings. Basic descriptive geometry. Computer-aided design as a design tool. Introduction to design for manufacturability. Emphasis of group work and peer review in the production of part for assemblies. Conceptual design projects presented in technical drawing format. Computer Laboratory.
กระบวนการออกแบบ และเครื่องมือทางด้านกราฟฟิคสำหรับการสื่อสารเบื้องต้นที่ใช้โดยวิศวกร การบันทึกเอกสารของการออกแบบโดยการวาดด้วยมือ และการวาดเชิงวิศวกรรม หลักการพื้นฐานของเรขาคณิตเชิงพรรณนา การใช้เครื่องมือทางคอมพิวเตอร์ช่วยในการออกแบบ หลักการเบื้องต้นของการออกแบบเพื่อกระบวนการผลิต เน้นการทำงานเป็นกลุ่ม และการวิจารณ์โดยเพื่อร่วมกลุ่มสำหรับการผลิตชิ้นส่วนเพื่อการประกอบ โครงงานการออกแบบแนวความคิดที่นำเสนอผ่านแบบทางวิศวกรรม และการทำปฏิบัติการผ่านเครื่องคอมพิวเตอร์
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. Read and interpret engineering drawings. Demonstrate the use of terminology and symbols used in engineering communications.
อ่านและอธิบายแบบวิศวกรรม และแสดงให้เห็นถึงความสามารถในการใช้งานคำศัพท์ และสัญลักษณ์ในการสื่อสารเชิงวิศวกรรม
CLO2. Create engineering drawings. Construct engineering communication documents describing mechanical devices and systems by using points, vectors, and surfaces.
เขียนแบบทางวิศวกรรม และสร้างเอกสารที่ใช้ในการสื่อสารซึ่งประกอบด้วยการอธิบายอุปกรณ์เชิงกล และระบบผ่านจุด เวกเตอร์ และพื้นผิว
CLO3. Select appropriate orthographic, sectional, auxiliary, and pictorial views, to convey engineering design concepts to fabricators.
เลือกใช้ภาพฉายสองมิติ ภาพตัด ภาพช่วย และภาพสามมิติเพื่อสื่อสารแนวคิดของแบบทางวิศวกรรมให้กับผู้ผลิดได้อย่างเหมาะสม
CLO4. Construct appropriate dimensions and geometric tolerances to convey a part’s functional design requirements to fabricators.
กำหนดมิติ และความคลาดเคลื่อนทางเลขาคณิตเพื่อสื่อสารข้อกำหนดการออกแบบการทำงานของชิ้นส่วนได้อย่างเหมาะสม
CLO5. Calculate size tolerances necessary to ensure the functional relationship to multi-part assemblies.
คำนวณความคลาดเคลื่อนของขนาดที่จำเป็นเพื่อรับรองความสัมพันธ์ของการทำงานกับการประกอบชิ้นส่วนหลายชิ้นส่วนเข้าด้วยกัน
CLO6. Create and define a conceptual solution to an engineering problem.
สร้างและกำหนดแนวคิดวิธีแก้ไขปัญหาทางวิศวกรรม
CLO7. Use a common industrial CAD package to create engineering documentation.
ใช้โปรแกรมสำเร็จรูปช่วยการออกแบบเพื่อสร้างเอกสารแบบทางวิศวกรรม
รายวิชาศึกษาเรื่องกระบวนการหลักของการผลิต โดยจะแสดงให้เห็นถึงกระบวนการจากการออกแบบสู่การเป็นผลิตภัณฑ์ โดยรายวิชาจะพูดถึงการเข้าใจกระบวนการผลิตในอุตสาหกรรม และเชื่อมโยงความต้องการด้านการออกแบบของชิ้นส่วนกับกระบวนการผลิตที่เหมาะสม รายวิชาจะอภิปรายถึงวิธีการที่การใช้ประโยชน์จากกระบวนการผลิตผ่านคุณสมบัติของวัสดุ และวิชานี้จะเน้นถึงคำแนะนำที่สำคัญในการออกแบบที่ส่งผลให้กระบวนการผลิตประสบผลสำเร็จ รายวิชามีโครงงานปฏิบัติการเพื่อจำลองหลักการการออกแบบ
This course is a study for the main manufacturing processes. It will illustrate how a design is turned into a product. It will offer a detailed understanding of manufacturing processes used in industry and will relate the design requirements of a part to the possible manufacturing processes. The course will also discuss how the material properties of a product control the spectrum of manufacturing processes that can be utilized and will highlight major design guidelines for each manufacturing process to be successful. A laboratory project is included to mimic the design principles.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. เชื่อมโยงประเภทวัสดุกับกระบวนการแปรรูป
Correlate the material type with the possible fabrication processes.
CLO2. อธิบายการปฏิบัติงานและเครื่องมือหลักในกระบวนการผลิต
Describe the operations and tools for major manufacturing processes.
CLO3. แสดงให้เห็นถึงตัวแปรในการออกแบบเพื่อกำจัดผลิตภัณฑ์ที่มีข้อบกพร่อง
Highlight the process design parameters to eliminate defective products.
CLO4. ตรวจสอบแบบทางวิศวกรรมของชิ้นส่วนและอธิบายถึงขั้นตอนกระบวนการผลิตที่เป็นไปได้ในการผลิตชิ้นส่วนนั้น
Examine the design drawing of a component and describe a feasible sequence of manufacturing processes for production of the component.
This course is a project-based study for selecting machine elements and designing equipment and tooling. Learners will work on joint projects from initial specification to scheme suggestion. Specific requirements will differ depending on the nature of the project. Learners need to use their creative thinking skill to generate and critical thinking skill to judge the ideas. Projects include the challenges that require application of math, science, and engineering knowledge; analytical and design procedures; communication skills; combined with ethical behavior of the individuals in each team.
รายวิชานี้เป็นรายวิชาโครงงานสำหรับการเลือกองค์ประกอบของเครื่องจักรและการออกแบบอุปกรณ์และเครื่องมือ ผู้เรียนจะทำโครงงานบูรณาการจากข้อกำหนดและความต้องการเพื่อเสนอแนวทาง โดยความต้องการเฉพาะจะแตกต่างไปตามแต่ละโครงงาน ผู้เรียนจะต้องใช้ความสามารถในการคิดอย่างสร้างสรรค์เพื่อเสนอแนวความคิด และใช้ทักษะการคิดเชิงวิพากษ์เพื่อตัดสินแนวความคิด โครงงานจะประกอบไปด้วยความท้าทายที่ต้องประยุกต์ใช้ทักษะด้านคณิตศาสตร์ วิทยาศาสตร์ และอาจรวมถึงความรู้ด้านวิศวกรรมอื่น ๆ ประกอบกับการวิเคราะห์และออกแบบขั้นตอน ทักษะด้านการสื่อสาร รวมถึงการทำงานอย่างมีจรรยาบรรณวิชาชีพในกลุ่มของตนเอง
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. รวบรวมข้อมูลที่สำคัญและความต้องการชิ้นส่วนเครื่องจักรกลจากขนาดมิติและรูปร่างของชิ้นส่วน, และมาตรฐานต่าง ๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้องได้
(Collect important information and needs of machine components from part drawing and dimension, and relevant standards, etc.)
CLO2. วิเคราะห์ความต้องการของผู้ใช้เครื่องจักร ความสามารถในการผลิตของชิ้นส่วนเครื่องจักรกล กลศาสตร์วัสดุ และกลไกต่างๆ
(Analyse machine-user requirements, manufacturability of mechanical components, mechanics of materials, and mechanisms.)
CLO3. ออกแบบเครื่องมือและเครื่องจักรตามความจำเป็น ข้อจำกัด รวมถึงความต้องการอื่น
(Purpose design of tooling and equipment by considering the constraints, needs, and other requirements.)
CLO4. ตรวจสอบทางเลือกโดยการทดสอบทางกล ทดลอง หรือจำลองการทำงาน
(Verify the solution by performing mechanical, functional, or simulation tests.)
CLO5. ใช้โปรแกรมออกแบบและวิเคราะห์ทางวิศวกรรม เช่น CAD, CAM and CAE เพื่อช่วยออกแบบเครื่องมือและอุปกรณ์
(Use CAD, CAM, CAE to support the design of tooling and equipment.
CLO6. พิจารณาผลกระทบของการแก้ปัญหาทางวิศวกรรมในบริบทของโลก เศรษฐกิจ สิ่งแวดล้อม และสังคม (Consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts.)
CLO7. มีความรับผิดชอบต่องานทางด้านวิศวกรรมที่ได้รับมอบหมาย
(Responsible for tasks relating with engineering profession.)
CLO8. ใช้ข้อมูลสนับสนุนที่ช่วยให้การสื่อสารมีคุณภาพสูงขึ้น
(Use supporting information that enables quality of communication.)
CLO9. ใช้ภาษาเหมาะสมกับผู้รับสาร (Use language appropriate to the audience.)
CLO10. ใช้ความรู้ที่มีอยู่เดิมกับสถานการณ์ใหม่ได้ (Apply existing knowledge to new situations.)
CLO11. มีส่วนร่วมกับการสร้างบรรยากาศการมีส่วนร่วมในการทำงาน
(Participate in creating a participatory atmosphere at work.)
Description
This course is a project-based study for Smart Manufacturing Data Managementstack. This project concludes the core concept of the stack where the learner should propose an information technology solution to the problem and take the idea of data management and analysis as part of an automated system instead of a traditional labor-intensive system. Learners will work on joint projects from given requirements to develop a solution for data management and analysis for modern manufacturing process. Specific requirements will differ depending on the nature of the project. Learners need to use their creative thinking skill to generate and critical thinking skill to judge the ideas. Projects include the challenges that require application of data collection, database management, data analysis, and data visualization in manufacturing where the learner must consider the used of information technology to modernize the process; analytical and design procedures; communication skills; combined with ethical behavior of the individuals in each team.
รายวิชานี้เป็นรายวิชาโครงงานสำหรับกลุ่มวิชาด้านการจัดการข้อมูลในการผลิตอัจฉริยะ รายวิชานี้สรุปแนวคิดสำคัญที่เกี่ยวข้องผ่านการทำโครงงาน ซึ่งผู้เรียนจะต้องเสนอแนวทางแก้ไขปัญหาด้วยเครื่องมือทางเทคโนโลยี สารสนเทศ และใช้แนวคิดการจัดการข้อมูลและการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลแบบอัตโนมัติมาทดแทนการทำงานแบบใช้แรงงาน ผู้เรียนจะทำโครงงานบูรณาการจากข้อกำหนดและความต้องการ เพื่อเสนอแนวทางและพัฒนาระบบการจัดการข้อมูลสำหรับกระบวนการผลิตสมัยใหม่ โดยความต้องการเฉพาะจะแตกต่างไปตามแต่ละโครงงาน ผู้เรียนจะต้องใช้ความสามารถในการคิดอย่างสร้างสรรค์เพื่อเสนอแนวความคิดและใช้ทักษะการคิดเชิงวิพากษ์เพื่อตัดสินแนวความคิด โครงงานจะประกอบไปด้วยความท้าทายที่ต้องความรู้ด้านการเก็บข้อมูล การจัดการฐานข้อมูล การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล และการแสดงผลข้อมูลในการผลิต ซึ่งผู้เรียนจะต้องคำนึงถึงการใช้งานด้านเทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศเพื่อทำให้กระบวนการมีความทันสมัย การวิเคราห์และออกแบบกระบวนการ การใช้ทักษะด้านการสื่อสาร รวมถึงการทำงานอย่างมีจรรยาบรรณวิชาชีพในกลุ่มของตนเอง
Courses Learning Outcones(CLOs)
1. Gather relevant information about the data storage processes and data analysis of the current production system.
2. Analyse data to identify problems and find solutions for industrial data management, data communication, or data visualization through information systems for decision-making in industrial production processes.
3. Propose solutions to problems that represent the use of information technology or modern technology to manage, store, analyse and display information that improves or develop production processes in industry.
4. Verify the proposed data management, data communication, or data visualization system by conducting appropriate experiment.
5. Use appropriate tools to collect and control data communication between equipment in industrial production processes.
6. Consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts.
7. Responsible for tasks relating with engineering profession.
8. Use language appropriate to the audience.
9. Use graphic that helps the understanding of the audience.
10. Apply existing knowledge to new situations.
11. Contribute to the creation of team goals and plans.
ผลสัมฤทธิ์การเรียนรู้
1. รวบรวมข้อมูลที่เกี่ยวข้องเกี่ยวกับกระบวนการจัดเก็บและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลของระบบการผลิตในปัจจุบัน
2. วิเคราะห์การจัดการข้อมูล การสื่อสารข้อมูล หรือการแสดงข้อมูลผ่านระบบสารสนเทศ เพื่อใช้ประกอบการตัดสินใจในกระบวนการผลิตอุตสาหกรรม
3. เสนอแนวทางแก้ไขปัญหาที่แสดงถึงการใช้เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศ หรือเทคโนโลยีสมัยใหม่ในการจัดการ จัดเก็บ วิเคราะห์ และแสดงผลข้อมูลที่ช่วยปรับปรุง หรือพัฒนากระบวนการผลิตในอุตสาหกรรม
4. ตรวจสอบระบบการจัดการข้อมูล การสื่อสารข้อมูล หรือการแสดงข้อมูลโดยทำการทดลองที่เหมาะสม
5. ใช้เครื่องมืออย่างเหมาะสมในการจัดเก็บข้อมูล และควบคุมการสื่อสารข้อมูลระหว่างอุปกรณ์ในกระบวนการผลิตทางอุตสาหกรรม
6. พิจารณาผลกระทบของการแก้ปัญหาทางวิศวกรรมในบริบทของโลก เศรษฐกิจ สิ่งแวดล้อม และสังคม
7. ความรับผิดชอบต่องานทางด้านวิศวกรรมที่ได้รับมอบหมาย
8. ใช้ภาษาเหมาะสมกับผู้รับสาร
9. ใช้สื่อกราฟฟิกที่ช่วยสร้างความเข้าใจแก่ผู้รับสาร
10. ใช้ความรู้ที่มีอยู่เดิมกับสถานการณ์ใหม่ได้
11. มีส่วนร่วมกับการสร้างเป้าหมายและแผนการทำงานของทีม
Course description
The capstone provides an opportunity for learners to integrate and apply knowledge from their academic studies, through the comprehensive evaluation of core modules in the curriculum of design of mechanical elements, design of mechanism, manufacturing process design, automated system design, manufacturing system design, quality and manufacturing competitiveness, and all learned fields. Course content delivered by the faculty mentor, based on real-world project. Learners present the entire study at the final class meeting. In addition to guidance from faculty mentor, your academic mentor from the anchor discipline will provide additional guidance and feedback through this phase of the study. The culminating product is the complete written report of the investigation and a formal presentation on the project to a professional audience of faculty mentors and other peers. Leaners are expected to be able to answer questions about their research and engage in professional dialogue about the topic during the formal presentation.
รายวิชานี้จะให้โอกาสผู้เรียนในการรวมความรู้ในการศึกษาและนำไปใช้ผ่านการประเมิน อย่างครอบคลุมของชุดวิชาหลักในหลักสูตรซึ่งประกอบไปด้วยการออกแบบองค์ประกอบกลไก การออกแบบ กลไก การออกแบบกระบวนการผลิต การออกแบบระบบอัตโนมัติ การออกแบบระบบการผลิต การควบคุม คุณภาพและขีดความสามารถการผลิต และแขนงที่ผู้เรียนได้ศึกษามา เนื้อหารายวิชาจะถูกสอนโดยคณาจารย์ที่ ทำหน้าที่เป็นที่ปรึกษาโดยอิงจากโครงงานจริงในอุตสาหกรรม ผู้เรียนนำเสนองานที่ได้ศึกษามาทั้งหมดในช่วง สุดท้ายของรายวิชา นอกเหนือจากคำแนะนำจากอาจารย์ที่ปรึกษา คำแนะนำจากที่ปรึกษาด้านวิชาการในด้าน ที่เกี่ยวข้องจะช่วยชี้แนะและให้ข้อมูลป้อนกลันแก่ผู้เรียน ผลิตผลสุดท้ายของโครงงานประกอบด้วยรายงานของ การศึกษา การนำเสนอโครงงานอย่างเป็นทางการแก่ผู้ฟังที่ประกอบไปด้วยคณาจารย์ และกรรมการ ผู้เรียน ต้องสามารถตอบคำถามเกี่ยวกับการศึกษาของตนเอง และมีส่วนร่วมในการโต้ตอบเกี่ยวกับหัวข้อการศึกษานั้น อย่างเป็นมืออาชีพ
Learning Outcomes
1. Identify engineering problems based on the principles of math, science, and engineering.
2. Analyse complex engineering problems considering the areas of materials and manufacturing processes.
3. Analyse complex engineering problems considering the areas of tooling engineering.
4. Analyse complex engineering problems considering the need of industrial automation systems.
5. Analyse complex engineering problems considering the effiency of manufacturing systems.
6. Analyse complex engineering problems considering the areas of quality and waste reduction.
7. Analyse complex engineering problems considering the need of information technology solutions for data management.
8. Develop solutions based on applying principles of math, science, and engineering.
9. Deliver an engineering solution that meet desired needs within realistic constraints.
10. Consider the impact of engineering solutions in global, economic, environmental, and societal contexts.
11. Develop and conduct appropriate experimentation, analyse and interpret data by the use of engineering judgment to draw conclusions.
12. Implement engineering project management considering contemporary issues.
13. Demonstrate responsibilities and ethics throughout the project.
14. Effectively communicate to a range of audiences by the use of speaking, writing, and graphics.
15. Acquire and apply new knowledge as needed, using appropriate learning strategies.
16. Function effectively on a team whose members together provide leadership, create a collaborative and inclusive environment, establish goals, plan tasks, and meet objectives.
17. Use techniques, skills, and modern tools necessary for engineering practice.
Course description
Education that provides students with the opportunity to learn practical skills in a workplace. Students will work in the workplace approved by the School. There will be clear responsibilities and clear schedules. The duration of work is not less than 24 hours a week. The results and evaluation must be reported by the faculty and the job supervisor at the workplace.
การศึกษาที่ให้นักศึกษาได้มีโอกาสเรียนรู้ภาคปฏิบัติและฝึกฝนทักษะในสถานประกอบการ จริง โดยนักศึกษาจะเข้าทำงาน ฝึกฝนในสถานประกอบการที่สาขาวิชารับรอง โดยจะมีการกำหนดหน้าที่ รับผิดชอบและตารางการปฏิบัติงานที่ชัดเจน โดยมีระยะเวลาทางานในสถานประกอบการไม่ต่ำกว่า สัปดาห์ละ 24 ชั่วโมง โดยจะต้องมีการรายงานผลและประเมินผลโดยคณาจารย์และผู้ควบคุมงานของสถานประกอบการ
Learning outcomes
1. Apply a basic knowledge from study to practical work in workplace.
2. Work and responsibility in team working.
3. Apply modern technology in real workplace.
4. Communicate with various professions.
ผลสัมฤทธิ์การเรียนรู้
1. ประยุกต์ความรู้พื้นฐานจากการเรียนในการปฏิบัติงาน ณ สถานประกอบการได้
2. ทำงานเป็นทีมรับผิดชอบ ในงานที่ได้รับมอบหมาย
3. ใช้เทคโนโลยีที่ทันสมัยในสถานประกอบการ
4. สื่อสารกับบุคคลหลายวิชาชีพได
Description:
Fundamental concepts in statistical inference with application to engineering contexts. The topics include data presenting and analyzing, discrete probability distribution (binomial distribution, poison distribution) and continuous probability distribution (normal distribution, exponential distribution), sampling theory, confidence intervals and hypothesis testing, analysis of variance, regression and correlation, define and measure of Six Sigma for statistical process control tools. Practice of commercial software in aiding of statistical analysis.
แนวความคิดพื้นฐานของการใช้สถิติในบริบทของวิศวกรรมศาสตร์ โดยมีหัวข้อประกอบด้วยการนำเสนอและวิเคราะห์ข้อมูล การแจกแจงความน่าจะเป็นแบบไม่ต่อเนื่อง (การแจกแจงแบบทวินาม การแจกแจงแบบปัวซอง) และการแจกแจงความน่าจะเป็นแบบต่อเนื่อง (การแจกแจงมาตรฐาน การแจกแจงแบบเลขชี้กำลง) ทฤษฎีการสุ่ม การกำหนดและวัดซิกซิกม่าสำหรับการใช้งานเครื่องมือในการควบคุมกระบวนการผลิตด้วยสถิติ การฝึกปฏิบัติซอฟท์แวร์เชิงพาณิชย์เพื่อช่วยในการวิเคราะห์สถิติ
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. Match types of data with distributions.
เลือกชนิดของข้อมูลกับประเภทการกระจายตัวของข้อมูลให้เหมาะสมกับสถานการณ์
CLO2. Select statistics and methodologies to model for basic hypothesis testing.
เลือกวิธีการทางสถิติเพื่อสร้างแบบจำลองสำหรับการทดสอบสมมติฐาน
CLO3. Classify and select appropriate data presentations such as table and diagram presentations.
ระบุและเลือกวิธีการนำเสนอข้อมูลที่เหมาะสม เช่น การนำเสนอแบบตารางและไดอะแกรม
CLO4. Apply appropriate software to communicate effectively of the data presentations and to model the basic hypothesis testing.
นำซอฟท์แวร์ที่เหมาะสมมาใช้ในการสื่อสารเพื่อนำเสนอข้อมูลและทดสอบสมมติฐานได้อย่างเหมาะสม
CLO5. Identify the statistics for define and measure of Six Sigma for statistical process control.
ระบุกระบวนการทางสถิติสำหรับการกำหนดและวัดค่าซิกซิกม่าสำหรับการควบคุมกระบวนการผลิตด้วยสถิติ
Description:
การประยุกต์ใช้หลักการของลีนในกระบวนการผลิต กระบวนการให้บริการเพื่อพัฒนา ผลผลิต เพิ่มมูลค่าและกำจัดของเสียรวมไปถึงการใช้วิธีการแก้ปัญหาแบบซิกซ์ซิกม่าเพื่อลดความแปรปรวนและ เพิ่มคุณภาพ การใช้การควบคุมกระบวนการด้วยสถิติและวิธีการวิเคราะห์ในทั้งสองกระบวนการ เนื้อหาที่ เกี่ยวข้องประกอบด้วย วิธีการสร้างกระบวนแบบลีน การพิสูจน์แนวทางการแก้ปัญหาแบบลีน การจัดการ เปลี่ยนแปลงสู่การทำลีน การนำซิกซ์ซิกม่าหรือลีนซิกซ์ซิกม่าไปใช้ การนำห้าระยะของกระบวนการซิกซ์ซิกม่า DMAIC ไปปฏิบัติ
Application of lean principles to manufacturing, service processes in order to improve productivity, increase value and eliminate waste as well as the use of the Six Sigma problem solving methodology to reduce variation and improve quality. The SPC tools and analysis methods used in both approaches. The topics covered include: methods for creating Lean processes, proven lean problem-solving methodologies, managing a lean transformation, implementing a Six Sigma or Lean Six Sigma (LLS) initiative, and executing the five phases of the Six Sigma DMAIC process.
Course Learning Outcomes:
CLO1. อภิปรายถึงวิธีการสร้างและทำให้คงไว้ซึ่งวัฒนธรรมที่มุ่งเน้นการส่งมอบมูลค่าให้แก่ ลูกค้าโดยการใช้เทคนิคด้านการพัฒนาต่อเนื่องและกลยุทธ์การลดความแปรปรวน (Discuss how to create and sustain a culture that focuses on the delivery of value to the customer by utilizing continuous process improvement and variance reduction strategies.)
CLO2. ถอดความหมายของข้อมูลป้อนกลับจากลูกค้าและเป้าหมายขององค์กรให้กลายเป็น โอกาสในการพัฒนา (Translate customer feedback and enterprise goals into opportunities for improvement.)
CLO3. อธิบายความแตกต่างและความคล้ายคลึงระหว่างกระบวนการลีนกับซิกซ์ซิกม่า และ อธิบายว่าทั้งสองกระบวนการเกื้อหนุนซึ่งกันและกันอย่างไร รวมถึงทั้งสองกระบวนการ สามารถถูกนำไปใช้เพื่อผลประโยชน์ที่สูงขึ้นได้อย่างไร(Explain the differences and similarities between Lean and Six Sigma, how they complement one another and how they can be used together for greater benefit.)
CLO4. อธิบายขั้นตอนกระบวนการการเลือกโครงงานและตั้งเป้าหมายสำหรับโครงงานซิกซ์ ซิกม่าหรือลีนซิกซ์ซิกม่า (Explain the project selection process and set goals for a Six Sigma or LSS project.)
CLO5. อธิบายถึงเป้าหมายแต่ละระยะของกระบวนการซิกซ์ซิกม่า DMAIC และสร้างแผนการ จัดการและดำเนินโครงงานการพัฒนาด้วยซิกซ์ซิกม่า (Explain the goals of each phase of the Six Sigma DMAIC process and create a plan for managing and executing a Six Sigma improvement project.)
CLO6. อธิบายถึงหน้าที่และความรับผิดชอบของสมาชิกกลุ่มโครงงานซิกซ์ซิกม่า และลำดับขั้น ของการพัฒนาทีม เครื่องมือในการช่วยตัดสินใจของทีม และกระบวนการสื่อสารของ ทีม (Explain the roles and responsibilities of Six Sigma project team members, the stages of team development, common team decision making tools and team communication methods.)
CLO7. เลือกและประยุกต์ใช้เครื่องมือและวิธีการวิเคราะห์ที่แพร่หลายซึ่งเป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ กระบวนการลีนซิกซ์ซิกม่า DMAIC (Select and apply the tools and analysis methods commonly used as part of the Lean Six Sigma DMAIC process.)
ENG35 4072 Big Data for Smart Manufacturing
This course focus on developing skills related to database and data analytics for manufacturing, which includes reading database schema and identifying relationship among the data entity and analyzing the data to extract knowledge using exploratory data analysis approach. The learners will grasp the idea of implementing the skills in a bigger system, such as SCM and ERP.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. Use database theory to design database schema for storing essential manufacturing data.
CLO2. Interpret database schema and explain the relationship of data entity.
CLO3. Use statistical theory and information technology tools to analyze the data in the database to extract knowledge or key information from the dataset.
CLO4. Verify the result of data analysis on the aspect of result validity, correctness of intepretation, and requirement compliance.
ENG35 4073 Smart Manufacturing Monitoring System
This course focus on explaining the cloud computing service in the context of Industrial IoT and developing a monitoring system for smart manufacturing through an open-source software. The course also focus on communication from the service to various devices in the system for data acquisition.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1. Explain architecture of monitoring service as part of a cloud computing system
CLO2. Integrate sensors, actuators, and controllers data into a cloud monitoring system **MOVE**
CLO3. Develop monitoring dashboard using provided tools to meet the specified requirements.
CLO4. Use data visualization techniques to develop components as part of the monitoring dashboard
CLO5. Use appropriate tools to collect and control data communication between equipment in industrial production processes.
วิชาบังคับก่อน : ไม่มี
หลักสูตรนี้มุ่งเน้นไปที่การประมวลผลภาพและการมองเห็นของคอมพิวเตอร์ ซึ่งเน้นไปที่การศึกษาวิธีการที่ช่วยให้เครื่องจักรมีความสามารถในการเรียนรู้และวิเคราะห์ภาพและวิดีโอ หัวข้อที่จะกล่าวถึง ได้แก่ ความรู้เบื้องต้นเกี่ยวกับการประมวลผลภาพและการมองเห็นด้วยคอมพิวเตอร์ ประเภทและรูปแบบของภาพดิจิทัล การกำหนดขอบเขตเงื่อนไข การประมวลผลภาพโดยการเปลี่ยนแปลงรูปร่างหรือโครงสร้างของภาพ การปรับปรุงคุณภาพของภาพ เทคนิคการปรับตั้งค่ากล้องและแสง เทคนิคการรู้จำรูปร่างและรู้จำรูปแบบ การตรวจจับ ตัดแบ่งขอบเขต ระบุตำแหน่ง และรู้จำวัตถุที่ต้องการในภาพ การเขียนโปรแกรมคอมพิวเตอร์สำหรับการมองเห็นของเครื่องจักร การเชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ควบคุมกับระบบการมองเห็นของเครื่องจักร โครงงานออกแบบระบบมองเห็นของเครื่องจักร
ผลสัมฤทธิ์การเรียนรู้
- อธิบายหลักการการประมวลภาพและการควบคุมระบบการมองเห็นของเครื่องจักร
- เขียนโปรแกรมเพื่อเชื่อมต่ออุปกรณ์ควบคุมกับระบบมองเห็นของเครื่องจักรได้
- ประยุกต์ใช้ความรู้การประมวลผลภาพและคอมพิวเตอร์วิทัศน์ในการแก้ปัญหาการมองเห็นของเครื่องจักรที่ได้รับมอบหมายได้
Image Processing and Computer Vision
Prerequisite : none
This course focuses on image processing and computer vision focuses on studying methods that allow a machine to learn and analyze images and video. Topics to be covered include introduction to image processing and computer vision, digital image type and format, boundary description, image enhancement, camera and lighting adjusting technique, technique on shape recognition and pattern recognition, object detection, image segmentation, specify the location, and object recognition in the image, computer program for machine vision, interface machine vision with controller, design machine vision projects and apply machine vision systems to solving engineering problems.
Learning outcomes
- Describe principles of image processing and machine vision control.
- Write computer program for connecting controller and machine vision system.
- Apply computer vision and image processing knowledge to designing and implementing algorithms to a given machine vision problem.

This course emphasizes academic, text-based and themed reading from different disciplines. The reading process, which requires critical thinking and decision-making in the use of evidence, sources, and rhetorical modes is introduced through various types of learning activities and class discussions.
By the end of the course, students will be able to
- recognize different genres of reading passages
- identify the main ideas and details of the passages
- demonstrate critical thinking and reading skills by writing summaries and expository paragraphs and essays in response to course readings
ศึกษาการออกแบบอัลกอริทึมที่ใช้แนวคิดเชิงนามธรรมเพื่อแก้ปัญหาหรืออธิบายการทำงานที่พบในชีวิตจริง การออกแบบและเขียนโปรแกรมที่มีการใช้ตัวแปร เงื่อนไข วนซ้ำ การออกแบบอัลกอริทึม เพื่อแก้ปัญหาทางคณิตศาสตร์ วิทยาศาสตร์อย่างง่าย การเขียนโปรแกรมโดยใช้ซอฟต์แวร์ Scratch, python, java และ c เป็นต้น ศึกษาการรวบรวมข้อมูลจากแหล่งข้อมูลปฐมภูมิ ประมวลผล สร้างทางเลือก ประเมินผล ตลอดจนใช้เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศอย่างปลอดภัย การจัดการอัตลักษณ์ การพิจารณาความเหมาะสมของเนื้อหา ใช้สื่อและแหล่งข้อมูลตามข้อกำหนดและข้อตกลงได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
โดยอาศัยกระบวนการเรียนรู้โดยใช้การคิดเชิงคำนวณและปัญหาเป็นฐาน (Problem – based Learning) เพื่อเน้นให้ผู้เรียนได้ลงมือปฏิบัติ ฝึกทักษะการคิด เผชิญสถานการณ์การแก้ปัญหาวางแผนการเรียนรู้ ตรวจสอบการเรียนรู้ และนำเสนอผ่านการทำกิจกรรมโครงงาน เพื่อให้เกิดทักษะ ความรู้ ความเข้าใจ และทักษะในการวิเคราะห์โจทย์ปัญหา จนสามารถนำเอาแนวคิดเชิงคำนวณมาประยุกต์ใช้ในการสร้างโครงงานได้
เพื่อให้ผู้เรียนมีความรู้ความเข้าใจ การนำข้อมูลปฐมภูมิเข้าสู่ระบบคอมพิวเตอร์ วิเคราะห์ ประเมิน นำเสนอข้อมูลและสารสนเทศ ได้ตามวัตถุประสงค์ ใช้ทักษะการคิดเชิงคำนวณในการแก้ปัญหาที่พบในชีวิตจริง และเขียนโปรแกรมอย่างง่าย เพื่อช่วยในการแก้ปัญหา ใช้เทคโนโลยีสารสนเทศและการสื่อสารอย่างรู้เท่าทันและรับผิดชอบต่อสังคม ตลอดจนนำความรู้ความเข้าใจในวิชาวิทยาศาสตร์ และเทคโนโลยีไปใช้ให้เกิดประโยชน์ต่อสังคม และการดำรงชีวิต จนสามารถพัฒนากระบวนการคิดและจินตนาการ ความสามารถในการแก้ปัญหาและการจัดการทักษะในการสื่อสาร และความสามารถในการตัดสินใจ และเป็นผู้ที่มีจิตวิทยาศาสตร์ มีคุณธรรม จริยธรรม และค่านิยมในการใช้วิทยาศาสตร์และเทคโนโลยีอย่างสร้างสรรค์
1. ข้อสอบมีทั้งหมด 65 ข้อ รวม 20 คะแนน โดยแสดงโจทย์ผ่านระบบ SUT e-learning
ตอนที่ 1 การสืบพันธุ์ของพืชดอก แบบตัวเลือก มี 20 ข้อ
ตอนที่ 2 การควบคุมการเจริญเติบโตและการตอบสนองของพืช แบบตัวเลือก มี 20 ข้อ
ตอนที่ 3 โครงสร้างและการเจริญเติบโตของพืชดอก มี 25 ข้อ
2. ข้อสอบเป็นแบบสุ่ม นักเรียนไม่สามารถย้อนกลับมาทำได้
- ข้อสอบมีทั้งหมด 38 ข้อ รวม 24 คะแนน โดยแสดงโจทย์ผ่านระบบ SUT e-learning
- ให้เขียนชื่อ - นามสกุล ชั้น เลขประจำตัวนักเรียน ในกระดาษคำตอบทุกหน้า
- กระดาษคำตอบให้ใช้เป็นกระดาษเปล่าขนาด A4 เท่านั้น โดยต้องแสดงวิธีทำ การเติมคำตอบ และการคำนวณทั้งหมด ให้ทดในที่ว่างภายในกระดาษคำตอบ
- การถ่ายรูปกระดาษคำตอบ ต้องมีความคมชัด แสงสว่างเพียงพอ ไม่ตัด หรือขาดส่วนใดส่วนหนึ่งของกระดาษคำตอบออกไป
- ไม่อนุญาตให้นำหนังสือ หรือเนื้อหาข้อความอื่นใดที่เกี่ยวข้องกับรายวิชาเข้าในการสอบ
- อนุญาตให้ใช้เครื่องคิดเลขในการทำข้อสอบได้
สำหรับศึกษาเอกสารการสอน/ติวสอบ และ vdo
สำหรับนักศึกษาที่สนใจเข้า E-learning นี้
ขอให้ติดต่อขอรหัสในการเข้า ที่อีเมล supattra.jia@sut.ac.th อาจารย์ ดร.สุพัตรา เจียวก๊ก
หรือ นางสาวสิริกาญจน์ ทองไหม (พี่เฌอแตมป์) นะคะ
ทั้งนี้ E-learning นี้ เป็นส่วนหนึ่งของ กิจกรรมการเตรียมความพร้อมในการสอบ CEFR สำหรับนักศึกษา หลักสูตรวิทยาศาสตรบัณฑิต สาขาวิชาอนามัยสิ่งเเวดล้อม
กรณีนักศึกษาสาขาวิชาอื่นที่สนใจเข้าศึกษาข้อมูลสามารถติดต่อขอเข้า E-learning นี้ได้คะ
English for Communication I (IST30 1101)
Trimester 1/2021
Course coordinator: Dr. Sirinthorn Seepho
Contacts: E-mail: sirin@sut.ac.th and Tel.: 089-204-6963
Objectives:
1. To develop student’s ability for effective and natural communication in both
social and academic settings
2. To promote integrated skills with primary emphasis on listening and speaking
skills
3. To improve communication management and language learning strategies to
become effective communicators
4. To promote active learning in students through topics relevant to their
interests and experiences
5. To introduce autonomous learning using various up-to-date and useful
resources

To answer the principle of language learning in the present global society, the main purpose of this course is to encourage the students to acquire language for communicative purposes, which includes precise knowledge of vocabulary, sentence structure, and appropriate tone of voice according to culture and language manner of the native speakers. In addition, the content mainly concerns with the language in daily basis such as travelling, health and welfare, sport, entertainment, asking and receiving the helps and services by various activities in and outside classroom. Moreover, student will also be encouraged to use the language as an important stepping-stone to explore and enhance his/her own interested career path.

Objectives:

Learning area for this course emphasizes the ability to use English language to identify the main idea, analyze the essence, conclude, interpret and express opinions from listening and reading feature articles and materials as well as provide justifications and examples for illustration. Moreover, the students will learn how to reasonably communicate and fluently express their plans for various situations both formal and informal ways.
All language skills; speaking, listening, reading, and writing, are included in both individual and group practice activities such as writing reflection, self-evaluation, oral presentation, conversing meaningful dialogue, role-play, and skit. Group discussion will focus on explaining and discussing about the differences of lifestyles, thoughts, beliefs, original of customs, language structures, idioms, proverbs, saying between Thai and foreign cultures.

วิชาบังคับก่อน (Prerequisite):
ENG22 3007 วิศวกรรมจราจร และ
ENG22 3008 ปฏิบัติการวิศวกรรมจราจร
คำอธิบายรายวิชา (Course Description):
ระบบและหน้าที่ของทางหลวง เกณฑ์การออกแบบซึ่งประกอบด้วยลักษณะของ ยานพาหนะ ผู้ใช้ถนน และการจราจร ระยะมองเห็นปลอดภัยส าหรับองค์ประกอบของถนนและบริเวณทางแยก การวิเคราะห์ความจุและระดับการให้บริการของถนน การออกแบบองค์ประกอบของสายทางเชิงเรขาคณิต หลักการออกแบบทางแยกและทางต่างระดับ
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ที่คาดหวังระดับรายวิชา (Course Learning Outcomes):
- อธิบายและจำแนกทางหลวงตามหน้าที่
- อธิบายเกณฑ์การออกแบบซึ่งประกอบด้วยลักษณะของยานพาหนะ ผู้ใช้ถนน และการจราจร
- ประยุกต์ใช้หลักการทางวิทยาศาสตร์พื้นฐานในการประมาณระยะมองเห็นปลอดภัยสำหรับองค์ประกอบของถนนและบริเวณทางแยกได้
- วิเคราะห์หาความจุและระดับการให้บริการของถนน
- ออกแบบองค์ประกอบเชิงเรขาคณิตของสายทาง
- อธิบายหลักการออกแบบทางแยกและทางต่างระดับ
E-Learning สำหรับวิชา ENG25 3130 กลศาสตร์ของเครื่องจักรกล สำหรับนักศึกษาสาขาวิศวกรรมเครื่องกลชั้นปีที่ 3

Course Content
Practice on measurement instruments and control systems related to polymer processing machine including temperature and pressure measurement, coordinate measuring machine (CMM), proximity sensor, pneumatic system, hydraulic system and program logic control (PLC) system, proximity sensor, pneumatic system, hydraulic system and program logic control (PLC) system.
Course Learning Outcomes vs Program Learning Outcomes (Program Learning Outcomes) vs PI
PLO3: สามารถพัฒนาและดำเนินการตรวจสอบและทดสอบ ทดลองที่เหมาะสม วิเคราะห์และแปลผลข้อมูล โดยใช้วิจารณญาณทางวิศวกรรมพอลิเมอร์ เพื่อสรุปผลการทดลอง
CLO1: Able to apply basic science and engineering to describe basic principles of measuring instruments and control systems, related to polymer processing machines. (สามารถใช้พื้นฐานทางด้านวิทยาศาสตร์และวิศวกรรมศาสตร์อธิบายหลักการทำงานเบื้องต้นของเครื่องมือวัดและระบบการควบคุมเครื่องจักรในกระบวนการขึ้นรูปพอลิเมอร์) (report introduction or quiz) (PI3.2)
CLO2: Able to use measuring instruments appropriately and safely. (สามารถใช้อุปกรณ์วัด (sensor) ได้อย่างเหมาะและปลอดภัย) (PI3.1)
CLO3: Able to make the unit of proximity, pneumatic, and hydraulic system function properly and
safely (สามารถเชื่อมต่อหน่วยย่อยของตัววัด proximity ระบบนิวเมติกส์ และระบบไฮดรอลิกส์ได้อย่างถูกต้องและปลอดภัย) (PI3.1)
CLO4: Able to write command program to control the PLC system and make it function as desired and safely (สามารถเขียนชุดคำสั่งควบคุมการทำงานของระบบ PLC เพื่อให้หน่วยย่อยของระบบทำงานได้อย่างที่ต้องการและปลอดภัย) (PI3.1)
CLO5: Able to determine data that is appropriate to collect. (รู้ข้อมูลที่เหมาะสมในการบันทึก) (PI3.2)
CLO6: Able to calculate readout error of the instruments. (คำนวณค่าความผิดพลาดของข้อมูลจากการวัดได้) (PI3.3) (tolerance and acceptance limit)
PLO4: สามารถติดต่อสื่อสารในงานวิศวกรรมได้อย่างมีประสิทธิผลกับผู้รับที่หลากหลาย (ทั้งภาษาไทยและภาษาต่างประเทศ ด้วยวาจา การเขียนรายงาน การเสนอผลงาน แบบทางวิศวกรรม
CLO7: Grammarly write an academic short report in an appropriate technical style format covering all required topics. (สามารถเขียนรายงานทางวิชาการอย่างสั้นในรูปแบบทางเทคนิคและไวยกรณ์ที่เหมาะสม และหัวข้อรายงานครบถ้วนตามที่กำหนด) (ภาพรวมรายงาน) (PI4.1)
CLO8: Graphically present the results as graphs or tables, suitably. (นำเสนอผลจากการทดสอบในรูปแบบของกราฟ หรือ ตาราง ได้อย่างเหมาะสม) (PI4.2)

1. Description:
รายวิชานี้จะเรียนเกี่ยวกับพื้นฐานการใช้โปรแกรม AutoCAD เน้นการออกแบบและเขียน แบบชิ้นงานกลเป็นหลัก โดยจะเริ่มศึกษาเครื่องมือและฟังก์ชันพื้นฐานที่จำเป็น คำสั่งของโปรแกรม การเขียน รูปพื้นฐานในสองและสามมิติ การเขียนแบบโดยการวางหลายชั้น การสร้างเอกสารแบบสั่งงานสำหรับวิศวกร
Philosophy of computer-based design using AutoCAD emphasise on design and create mechanical parts. Study the function and essential commands of AutoCAD, basics of drawing in 2D and 3D, the practice of multiple layers for mechanical drawing.
2. Credits: 2(1-3-5)
3. Prerequisites or co-requisites:
None
4. Course Type: Technical Elective
5. Course Instructor: Asst. Prof. Dr. Prasert Aengchuan,
E-mail prasert.a@g.sut.ac.th, Tel. 4272
6. Classroom/Teaching Platform: Facebook Group, SUT e-Learning
Facebook Group: ENG35 4507 AUTOCAD FOR ENGINEERING
Google Classroom: ENG35 4507 AUTOCAD FOR ENGINEERING
7. Teaching-Learning Materials:
8. Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
CLO1 สามารถใช้โปรแกรมออโตแคดเขียนแบบรูปพื้นฐานในสองและสามมิติได้
Ability to apply AutaCAD package to create drawings in 2D and 3D.
CLO2 สามารถเขียนแบบโดยการวางหลายชั้นในออโตแคดได้
Ability to create multiple layers in AutoCAD.
CLO3 สามารถสร้างแบบทางวิศวกรรมให้เป็นไปตามมาตรฐานของแบบวิศวกรรมทาง อุตสาหกรรม
Ability to create mechanical drawings according to industry standards.
E-learning สำหรับนักศึกษาสาขาวิชาวิศวกรรมเมคคาทรอนิกส์ สำนักวิชาวิศวกรรมศาสตร์ ที่ลงทะเบียนเรียนในรายวิชา ENG51 0201 และ ENG51 0202

- ENG51 1701 AI Technology
- ENG51 1702 Computer Vision Technology
- ENG51 1703 Machine Learning
- ENG51 1704 Deep learning
- ENG51 1705 AI Project


รายวิชานี้มุ่งเน้นการประยุกต์ใช้เทคโนโลยีปัญญาประดิษฐ์ (AI) ในการวิเคราะห์และพัฒนางานวิศวกรรมโยธา เพื่อเสริมสร้างความสามารถในการออกแบบและแก้ไขปัญหาที่ซับซ้อนของวิศวกร ผู้เรียนจะได้ศึกษาแนวคิดพื้นฐานของปัญญาประดิษฐ์ เช่น การเรียนรู้ของเครื่อง (Machine Learning) ซึ่งประกอบด้วย Supervise Learning, Unsupervised Learning, Reinforcement Learning, และขั้นตอนการดำเนินการการเรียนรู้ของเครื่อง การวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลขนาดใหญ่ (Big Data) และการประมวลผลภาพ (Image Processing) โดยมุ่งเน้นไปทีการศึกษาแบบ Surpervise Learning อาทิ Linear Regression, Logistic Regression, Artificial Neural Network และ Convolutional Neural Network เป็นต้น เพื่อมุ่งนี้ให้สามารถต่อยอดนำไปใช้ในงานด้านวิศวกรรมโยธาและการบริหารงานก่อสร้าง นอกจากนี้ ผู้เรียนจะได้รับการฝึกปฏิบัติในการใช้ซอฟต์แวร์และแพลตฟอร์ม AI ที่เกี่ยวข้อง เพื่อพัฒนาความเข้าใจและสามารถนำไปประยุกต์ใช้ในงานวิศวกรรมโยธาได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ

Course Outline
Chain structure of polymer molecules, configurations and conformation of polymer chain, molecular weight and molecular size, amorphous state and crystalline state of solid polymers, models of chain conformation in amorphous state and crystalline state, crystalline morphology, thermal transitions, crystallization and kinetics of crystallization, thermal transitions, thermodynamics of fusion, solution process, thermodynamics of mixing and phase separation, viscoelasticity, time-temperature superposition, mechanical behavior, failure behavior, thermal properties, electrical properties, and optical properties
Course Responsibility to Program Learning Outcome
PLO1: An ability to apply knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering fundamentals for petrochemical and polymer engineering procedures or processes.
PLO2: An ability to analyze petrochemical and polymer engineering problems: Identify, formulate and research literature reaching the solution for complex engineering problems.
PLO8: An ability to understand and consider the impact of professional petrochemical and polymer engineering work to economics society environmental and sustainability
PLO11: Recognize the need for, and have ability to engage in life-long learning
|
CLO1:Be able to: classify and explain basic chain structure conformation, configuration and stereochemistry of polymer chains |
|
CLO2: Be able to interrelate structure to the properties of polymer |
|
CLO3: Be able to explain influence of factors/parameters on properties of polymers |
|
CLO4: Be able to use equation for predicting thermal transitions and solvation phenomena |
|
CLO5: Be able to demonstrate information on environmental and societal impact from source/resource consumption for polymeric material production to end use product |
|
CLO6: Be able to search relevant information from open source. |

Prerequisite : 105101 Physics I
Basic concepts. Thermodynamic properties, temperature, work and heat. First law. Second law, irreversibilities and entropy. Availability. Tables and charts of properties. Analyses of thermodynamic processes and cycles. Vapor and gas power cycles.
Learning outcomes
This course provides basic concepts of Thermodynamics. Student will be able to describe the basic concepts of Thermodynamics. Student will be able to determine properties of pure substances at different states from property tables. Student will be able to apply the first law of thermodynamics to analyze energy conversion in closed and open systems. Student will be able to apply the second law of thermodynamics and the Carnot cycle to evaluate the thermal efficiency and coefficients of performance for heat engines, refrigerators, and heat pumps. Student will be able to calculate the entropy changes that takes place during processes.

ENG85 2110 Mechanics of Materials I 3(3-0-6)
Prerequisite: ENG85 2030
Engineering Statics Forces and stresses; stress-strain relations; stresses in beams; shear diagram and moment diagram; deflection of beams; buckling of columns; Mohr’s circle and combined stresses; failure criteria.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
- Define solution procedures and methods by applying knowledge of mathematics, science and fundamental engineering in analysis and design of structures and structural members in Mechanics of Materials.
- Find appropriate problem solutions within reasonable constraints by applying the concept of free-body diagram, equations of equilibrium and mathematics in Mechanics of Materials problems.


ENG85 3031 Aircraft Structures 3(2-3-7)
Prerequisite: ENG85 2110 Mechanics of Materials I
The principles of deformation; stress and strain in materials; properties of materials; stress and strain relations; analysis of simple mechanical elements subjected bending shear and torsion; theories of failure; analysis of plate connection; principles of stressed skin analysis; analysis of the opened and closed thin-walled tubes; stress analysis of aircraft components including wing spars, box beams, fuselage and others.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
1. Understand the preliminary structure analysis and failure criteria;
2. Describe the failure parameters of structural analysis;
3. Understand limitations and range of applicability of mechanical and aircraft structural analysis;
4. Describe the plate theory; calculate deflections in thin plates and stress distribution;
5. Analyze for an outline suitable thin wall tube, wing, fuselage and features of mechanical parts or aircraft structural parts that will satisfy requirements or that appropriate to an action.

Objectives:
1. To develop student’s ability for effective and natural communication in both social and academic settings
2. To promote integrated skills with primary emphasis on listening and speaking skills
3. To improve communication management and language learning strategies to become effective communicators
4. To promote active learning in students through topics relevant to their interests and experiences
5. To introduce autonomous learning using various up-to-date and useful resource
This course aims at all essential language skills; listening, speaking, reading, and writing. The learners will expose the language through various learning materials and activities in order to acknowledge and understand the diversity of cultures, customs, traditions, thinking, and society of the world community. In addition, they will learn how to accurately read aloud texts, news, announcements, advertisements, poems and skits by observing the principles of reading. Moreover, class activities will encourage the learners to be able to converse and write to exchange data about themselves, various matters around them, experiences, situations, news or incidents, issues of interest and communicate them continuously and appropriately. The learns will learn how to choose and use requests, clarifications, explanations and give instructions; speak and write to show needs; offer and provide assistance; speak and write appropriately to ask for and give data, describe, explain, and compare. At the end of the course, the students are expected to be able to express their opinions about matters/issues/news/incidents, which they have heard and read by using register of language, tone of voice, gesture and manners appropriate to the level of the persons, time, occasions and places. Finally, the learners will learn how to conduct research/search, analyze, and conclude the data related to the learning areas from various sources.
This course aims at all essential language skills; listening, speaking, reading, and writing. The learners will expose the language through various learning materials and activities in order to acknowledge and understand the diversity of cultures, customs, traditions, thinking, and society of the world community. In addition, they will learn how to accurately read aloud texts, news, announcements, advertisements, poems and skits by observing the principles of reading. Moreover, class activities will encourage the learners to be able to converse and write to exchange data about themselves, various matters around them, experiences, situations, news or incidents, issues of interest and communicate them continuously and appropriately. The learns will learn how to choose and use requests, clarifications, explanations and give instructions; speak and write to show needs; offer and provide assistance; speak and write appropriately to ask for and give data, describe, explain, and compare. At the end of the course, the students are expected to be able to express their opinions about matters/issues/news/incidents, which they have heard and read by using register of language, tone of voice, gesture and manners appropriate to the level of the persons, time, occasions and places. Finally, the learners will learn how to conduct research/search, analyze, and conclude the data related to the learning areas from various sources.

ตารางเรียน วันศุกร์เวลา 13.00 -16.00 น. ห้อง B2104
FaceBook 67 การเขียน IAT31 1002 https://www.facebook.com/groups/3820453811548052
วัตถุประสงค์ เพื่อให้นักศึกษาทราบถึงหลักการ โครงสร้าง และรูปแบบการเขียนภาษาไทยเชิงวิชาการ และสามารถสื่อสารโดยการเขียน การใช้ภาษาไทยในการเขียนเชิงวิชาการได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ อีกทั้งพัฒนาทักษะการทำงานเป็นทีม การสื่อสาร การรู้จักตนเอง และเรียนรู้ด้วยตนเอง
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ Course Learning Outcome
- 1. นักศึกษาสามารถวิเคราะห์ และ ใช้ภาษาไทยในการเขียนตอบคำถามได้ตรงประเด็น
- 2. นักศึกษาสามารถใช้ภาษาไทยในการเขียนเชิงวิชาการทางวิทยาศาสตร์ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
- 3. นักศึกษามีการพัฒนาทักษะในศตวรรษที่ 21 โดยเฉพาะทักษะการทำงานเป็นทีมและทักษะการสื่อสาร
- 4. นักศึกษามีความรับผิดชอบต่อตนเองและผู้อื่น ตรงต่อเวลา และ มีระเบียบวินัย
- Students are able to analyze and use Thai to answer questions properly.
- Students are able to write scientific report effectively and efficiently.
- Students are able to improve their 21st century skills, especially teamwork and communication skills.
- Students learned to have better responsibility for themselves and others, better time management and discipline.

วัตถุประสงค์ เพื่อให้นักศึกษาทราบถึงหลักการ โครงสร้าง และรูปแบบการเขียนภาษาไทยเชิงวิชาการ และสามารถสื่อสารโดยการเขียน การใช้ภาษาไทยในการเขียนเชิงวิชาการได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ อีกทั้งพัฒนาทักษะการทำงานเป็นทีม การสื่อสาร การรู้จักตนเอง และเรียนรู้ด้วยตนเอง
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ Course Learning Outcome
1. นักศึกษาสามารถวิเคราะห์ และ ใช้ภาษาไทยในการเขียนตอบคำถามได้ตรงประเด็น
2. นักศึกษาสามารถใช้ภาษาไทยในการเขียนเชิงวิชาการทางวิทยาศาสตร์ได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ
3. นักศึกษามีการพัฒนาทักษะในศตวรรษที่ 21 โดยเฉพาะทักษะการทำงานเป็นทีมและทักษะการสื่อสาร
4. นักศึกษามีความรับผิดชอบต่อตนเองและผู้อื่น ตรงต่อเวลา และ มีระเบียบวินัย
- Students are able to analyze and use Thai to answer questions properly.
- Students are able to write scientific report effectively and efficiently.
- Students are able to improve their 21st century skills, especially teamwork and communication skills.
- Students learned to have better responsibility for themselves and others, better time management and discipline.

Backward journeys of food in the market. The course covers how food arrives at end users from the beginning, starting at farms and going backward in the sequence, exploring how science and technology are involved. This includes, for example, how food is stored on shelves, the management of food on shelves, delivery of food products from factories, food production on an industrial scale, preparation and preservation of raw materials for food production, delivery of raw materials from farms to factories, animal and crop production, harvesting processes, and obtaining animal and crop breeds. The emphasis is also on how food can be obtained from multiple production approaches such as safe agriculture and organic agriculture. The course highlights the fact that science and technology are involved in all processes and management. Furthermore, it emphasizes leading students to identify opportunities and risks in food supply chains and food businesses. It covers the evolution of technology and innovation involved, the effects of global changes on food businesses, and relevant regulations. This course serves as a brief introduction to the 4-year program.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students must be able to:
- Understand an overview of the food production chain and its significance in Food and Agriculture Business.
- Explain the linkages of science and technology in the food production chain and Agribusiness.
- Identify the opportunities and risks in the food production chain within the realm of food and agriculture.

The arts and sciences of foods, cooking, and food culture; biological and spiritual requirements of foods; foods as art forms, emotional experiences, traditions, and multicultural aspects; the evolution of food culture; and dining manners.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs):
Upon successful completion of this course, students must be able to:
1. Understand the food landscape from the perspective of energy and chemical sources of the body, as well as its form as an art and its significance in various cultures.
2. Understand the risks and opportunities associated with food innovation in both national and global contexts.
3. Apply creative thinking to generate innovative ideas related to food.

This course will focus on three areas as follow: 1) Food preservation using low heat (mild process) such as chilling or freezing, the reduction of water activity, drying, concentration and hurdle technology. 2)Food preservation using heat treatment such as pasteurization, cooking and blanching. 3) Food prevention using packaging.
Course Learning outcomes (CLOs)
Having successfully completed this course, student must be able to :
1. The students will be able to know and understand about technology in food preservation.
2. The students will be able to selected appropriate technology for food preservation.
IAT31 1206 Art of storytelling 3(2-3-4)
Prerequisite: None
This course will develop students to understand communication skills in various ways, focusing on learning the principles and procedures of communication. In order for students to be able to effectively convey the content or message they need in a complete process both online and on ground. Not only develop students to be media creators but also provides an understanding of the dimensions of design, creativity, and distribution by the application of information technology and computer.
Course Learning outcomes (CLOs)
Having successfully completed this course, student must be able to:
1. Understand the principles and procedures of communication.
2. Able to lecture, analyze, critique case.
3. Able to use information technology and computer for searching information and presentation.

This course presents communication skills and principles with a strong focus on message awareness. Learners will understand the views of the audience through various conditions and factors such as the process of understanding the media, understanding the meta model, as well as the assessment of the awareness situation to create the media and presentation to achieve their objectives in different situations by the application of information technology and computer. Students will also learn deep communication skills in various dimensions.
Course Learning outcomes (CLOs)
Having successfully completed this course, student must be able to :
1. Understand the principles with a strong focus on message awareness.
2. Understand the views of the audience through various conditions and factors.
3. Able to use information technology and computer for searching information and presentation.

IAT31 2218 Global disruptions and holistic development 3(2-3-4)
Prerequisite : None
This course offers students the opportunity to learn and understand the disruption in economic, social, cultural and perspective on the conditions of the modern world. Through examples of events, news and analyzing tools such as Scenario planning to understand the accelerating factors, supporting factors, leverage points by system thinking with the aid of information technology and computer.
Course Learning outcomes (CLOs)
Having successfully completed this course, student must be able to :
1. Understand patterns and have awareness of the substitution of global disruptions
2. Analyze the reasons and the effects of disputes that occurred in the past.
3. Analyze the events and their future effects from the current situation.
Leadership concepts; characteristics, skills, and roles of leaders. Self assessment of leadership, Roles of the founder and management, corporate culture, recruitment process, develop and retain human resources for small innovative businesses, and team development and team motivation are include.
Course Learning outcomes (CLOs)
Having successfully completed this course, student must be able to understand the Leadership concepts; characteristics, skills, and roles of leaders. Self assessment of leadership, Roles of the founder and management.

IAT32332661 Postharvest Physiology and Changes of Fresh Produce 3(3-0-6)
Prerequisite : Consent of the School
Physiological processes and postharvest changes of fresh produce relating to maturity of perishable crops, effects of postharvest handling on physiological processes and changes of fresh product, application of biotechnology in postharvest fields and case study of perishable produces.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
Having successfully completed the course, student must be able to:
- Learners can explain the changes in postharvest physiology of the produce.
- Learners can describe the effect of postharvest technology on changes in the postharvest physiology of products.
IAT32 6801 สัมมนามหาบัณฑิต 1 1(1-0-2)
วิชาบังคับก่อน : ไม่มี
การนำเสนอและอภิปรายเชิงปริทัศน์ ทางด้านพืชศาสตร์ที่เกี่ยวข้องกับวิทยานิพนธ์ระดับมหาบัณฑิต การคัดเลือกข้อมูลจากบทความ รายงานการวิจัย และแหล่งข้อมูลอื่น ๆ การคิดวิเคราะห์ และสรุปประเด็นสำคัญ
การจัดเตรียมสื่อประกอบการสัมมนาและบทคัดย่อ
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ที่คาดหวังระดับรายวิชา (CLOs)
นักศึกษาที่ผ่านรายวิชานี้มีความสามารถ ดังนี้
1.สืบค้นข้อมูลทางด้านพืชศาสตร์และศาสตร์อื่น ๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้อง และคัดเลือกเพื่อนำมานำเสนอในการสัมมนา รวมถึงใช้เพื่อการอภิปรายได้
2.วิเคราะห์และแปลความหมายทางสถิติ รวมถึงวิเคราะห์และสังเคราะห์องค์ความรู้ทางด้านพืชศาสตร์และศาสตร์อื่น ๆ ที่เกี่ยวข้อง เพื่อการสัมมนาและการอภิปรายได้
3.ใช้โปรแกรมประยุกต์ที่เหมาะสมในการจัดทำสื่อประกอบการสัมมนาและจัดทำบทคัดย่อใช้ รวมทั้งสามารถใช้ภาษาอังกฤษในการสื่อสารทั้งการเขียนบทคัดย่อ การสัมมนา และอภิปรายเนื้อหาที่เกี่ยวข้องได้
4.มีความรับผิดชอบ ตรงต่อเวลา และมีจรรยาบรรณทางวิชาการ
IAT32 6801 M.Sc. Seminar I 1(1-0-2)
Prerequisite : None
Presentation and discussion on reviewed articles on crop science subjects related to M.Sc. thesis topic. Selection, analysis, and summarization
of materials from articles, research reports, and other sources and create the presentation aids and abstract.
Course Learning Outcomes (CLOs)
1.Having successfully completed the course, the student must be able to:
2.Acquire the information on crop science and related fields and then select this information for a seminar and discussion.
3.Correctly interpret statistical data, as well as assess and synthesize information on crop science and related fields for a seminar and discussion.
4.Create a presentation and abstract using the appropriate software, and use English to prepare the abstract, deliver the presentation, and engage in related
topical discussion. Demonstrate responsibility, punctuality, and academic ethics.

Course Learning Outcome (CLO)
1. To understand the principle of biological processes at the molecular level.
2. To apply the basic knowledge of molecular biology for use in research processes related
3. To enhance student creativity and know how to apply knowledge to solve their problems in research processes related to molecular biological processes.

IAT34 5221 Molecular Biology (term 2/2567)
Mandatory Assignment:
Before class: *Read assigned pages from Lehninger Principles of Biochemistry, 4th Edition
Students should set aside time to read the assigned pages from the textbook and find more information about the topics) and do the Quiz (homework). The quiz will be given in e-learning at least 4 days before the due date. Please submit the quiz before 10 am
Tuesday
10.00-12.00 Ask questions (submit the home work)
Quiz/Answer the quiz (by key staff)
Thursday
9.30 - 9.50 Ask questions
10.00-11.00 Student presentation (assigned topic) 2 students/ week
11.00-12.00 Discussion (all)
Course Learning Outcome (CLO)
1. To understand the principle of biological processes at the molecular level.
2. To apply the basic knowledge of molecular biology for use in research processes related
3. To enhance student creativity and know how to apply knowledge to solve their problems in research processes related to molecular biological processes.

This course aims to:
1. To develop student’s ability for effective and natural communication in both social and academic settings
2. To promote integrated skills with primary emphasis on listening and speaking skills
3. To improve communication management and language learning strategies to become effective communicators
4. To promote active learning in students through topics relevant to their
interests and experiences
5. To introduce autonomous learning using various up-to-date and useful
resources

พัฒนาความสามารถของนักศึกษาในการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษเพื่อการสื่อสารในสังคมได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ บูรณาการทักษะภาษาอังกฤษโดยให้ความสำคัญกับทักษะการฟังและการพูด พัฒนากลยุทธ์การสื่อสารและกลยุทธ์การเรียนภาษา ส่งเสริมการเรียนรู้ภาษาอังกฤษด้วยตนเองโดยใช้แหล่งทรัพยากรที่หลากหลาย
Objectives:
1. To develop student’s ability for effective and natural communication in both social and academic settings
2. To promote integrated skills with primary emphasis on listening and speaking skills
3. To improve communication management and language learning strategies to become effective communicators
4. To promote active learning in students through topics relevant to their
interests and experiences
5. To introduce autonomous learning using various up-to-date and useful
resources
Objectives:
1. To develop student’s ability for effective and natural communication in both
social and academic settings
2. To promote integrated skills with primary emphasis on listening and speaking
skills
3. To improve communication management and language learning strategies to
become effective communicators
4. To promote active learning in students through topics relevant to their
interests and experiences
5. To introduce autonomous learning using various up-to-date and useful
resource
พัฒนาความสามารถของนักศึกษาในการใช้ภาษาอังกฤษเพื่อการสื่อสารในสังคมได้อย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ บูรณาการทักษะภาษาอังกฤษโดยให้ความสำคัญกับทักษะการฟังและการพูด พัฒนากลยุทธ์การสื่อสารและกลยุทธ์การเรียนภาษา ส่งเสริมการเรียนรู้ภาษาอังกฤษด้วยตนเองโดยใช้แหล่งทรัพยากรที่หลากหลาย
Developing students’ abilities of effective communication in social settings; focusing on integrated skills with the primary emphasis on listening and speaking; developing communication and language learning strategies; and promoting autonomous learning using various resources
คำอธิบายรายวิชา
พัฒนาความสามารถของนักศึกษาในระดับที่สูงขึ้น เพื่อการสื่อสารอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพทั้งในสถานการณ์ทางสังคมและวิชาการ บูรณาการทักษะโดยเฉพาะอย่างยิ่งทักษะการฟังและการพูดเพื่อจุดประสงค์เชิงวิชาการ พัฒนากลยุทธ์การสื่อสารและกลยุทธ์การเรียนภาษา สร้างเสริมการเรียนรู้ด้วยตนเอง โดยใช้เนื้อหากึ่งวิชาการจากแหล่งทรัพยากรที่หลากหลาย
Further developing students’ abilities for effective communication in social and academic settings; focusing on integrated skills, particularly listening and speaking for academic purposes; further developing communication and language learning strategies; and reinforcing autonomous learning using various semi-academic materials from a variety of resources
This course aims :
1. To develop student’s ability for effective and natural communication in both social and academic settings
2. To promote integrated skills with primary emphasis on listening and speaking skills
3. To improve communication management and language learning strategies to become effective communicators
4. To promote active learning student through topics relevant to their interests and experiences
5. To introduce autonomous learning using various up-to-date and useful resources

Objectives:
1. To develop student’s ability for effective and natural communication in both social and academic settings
2. To promote integrated skills with primary emphasis on listening and speaking skills
3. To improve communication management and language learning strategies to become effective communicators
4. To promote active learning student through topics relevant to their interests and experiences
5. To introduce autonomous learning using various up-to-date and useful resources

Learning theories and principles of technology-enhanced language learning (TELL); online resources and software for language learning; introduction to TELL authoring programs; brief overview of research on technology-enhanced language learning

This course focuses on developing language tests. It gives fundamental knowledge in order for the students to conduct research in areas related to language testing and assessment.
คำอธิบายรายวิชา (Course Description)
แนวคิดและความสำคัญของการพัฒนานวัตกรรมทางสังคม ปัญหาและความท้าทายของสังคมและสิ่งแวดล้อม กระบวนการคิดเชิงออกแบบเพื่อแก้ปัญหาทางสังคม การประเมินผลกระทบทางสังคม กรณีศึกษาของการพัฒนานวัตกรรมทางสังคมในศาสตร์สาขาต่าง ๆ
Concept and importance of social innovation development, environmental and social problems and challenges, design thinking for social problem solving, social impact assessment, case studies of social innovation development in different subjects
Course Learning Outcomes
1) วิเคราะห์ปัญหาและความท้าทายของสังคมและสิ่งแวดล้อมที่เป็นโอกาสทางธุรกิจที่จะสร้างผลกระทบทางสังคม
2) ประยุกต์ใช้กระบวนการคิดเชิงออกแบบเพื่อวิเคราะห์ กำหนดปัญหา
3) ประเมินผลกระทบทางสังคมของธุรกิจเพื่อสังคม/นวัตกรรมทางสังคม
This course is assigned for comprehensive examination of Master degree. The students will have the examination online through elearning platform.
NL-1 Basic Medical Sciences เป็นเนื้อหาการเรียนการสอนที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการสอบใบประกอบวิชาชีพแพทย์ หรือ National License ที่ให้การรับรองโดยศูนย์ประเมินและรับรองความรู้ความสามารถในการประกอบวิชาชีพเวชกรรม (ศรว.) ของแพทยสภา เพื่อให้มั่นใจได้ว่าบุคคลากรทางการแพทย์ของไทยมีมาตราฐานเดียวกันในระดับสากล
ดังนั้น NL-1 Basic Medical Sciences จึงเป็นการเรียนการสอนเพื่อให้นักศึกษาแพทย์ของ มทส. มีความรู้และเป็นการเตรียตัวสำหรับการประเมินความรู้พื้นฐาน ทางด้านเวชกรรมการแพทย์ (pre-clinic) โดยจะแบ่งเนื้อหาการเรียนออกเป็น B1-B11 ดังต่อไปนี้
- B1 : General Principles
- B2 : Hematopoietic and Lymphoreticular Systems
- B3 : Central and Peripheral Nervous Systems
- B4 : Skin and Related Connective Tissue
- B5 : Musculoskeletal System
- B6 : Respiratory System
- B7 : Cardiovascular System
- B8 : Gastrointestinal System
- B9 : Renal/Urinary System
- B10 : Reproductive System
- B11 : Endocrine System

(ภาษาไทย) กระบวนการพยาบาล หลักการและเทคนิคการประเมินภาวะสุขภาพ หลักการและขั้นตอนการรวบรวมข้อมูล การประมวลข้อมูลความรู้และหลักฐานเชิงประจักษ์ การวิเคราะห์สาเหตุ การตัดสินทางคลินิก การวินิจฉัยปัญหาสุขภาพ การกำหนดเป้าหมายและผลลัพธ์ทางการพยาบาล การออกแบบกิจกรรมการพยาบาล การประยุกต์ใช้กระบวนการพยาบาลและการประเมินผลลัพธ์ในสถานการณ์เสมือนจริง
(ภาษาอังกฤษ) Nursing process; principles and techniques of health assessment; principles and process of data collection; data processing, evidenced based data; cause analysis; clinical decision making; health problem diagnosis; setting goals and outcomes of nursing; designing nursing activities; applying the nursing process and evaluating outcomes in simulation-based learning.
903302 ทักษะทางคลินิกทันตกรรม (Clinical skill Development in Dentistry)
การเรียนรู้การเคลื่อนไหวของร่างกายที่เกี่ยวข้องกับงานคลินิกทันตกรรม หลักการทำงาน ด้วยการรับรู้การเคลื่อนไหวของกล้ามเนื้อและข้อต่อ และประยุกต์ในการปฏิบัติงานทันต กรรม หลักการปฏิบัติงานด้านทันตกรรมที่สอดคล้องกับหลักการยะศาสตร์ การกำหนดท่าทาง และตำแหน่งในการทำงานที่สมดุล การจัดสภาพแวดล้อม ในการทำงานที่ปลอดภัยและมี ประสิทธิภาพในการดูแลสุขภาพแก่ผู้ป่วย การใช้กระจกส่องปากอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ทักษะการใช้มือ ควบคู่ กับการมองเห็นและดุลยภาพบำบัดเพื่อการป้องกันและแก้ไขการบาดเจ็บของระบบ กล้ามเนื้อ และกระดูกของร่างกาย
Learning of psychomotor skills in related to dental clinical practice, proprioceptive derivation principle and its application in dental clinical practice, application of ergonomics in dentistry, identification of balanced working posture & position, setting safe & healthy working environment to deliver effective health care, effective use of mouth mirror, hand and eye coordination skill; practice in appropriate working posture & position setting up dental instrument, equipment and working environment, handling of mouth mirror and instrument for tooth preparation, cooperated practice between dentist and assistant including Mind Body (Equilibrium). Therapy for prevention and correction of musculoskeletal injuries.
DEN02 3003 ทักษะทางคลินิกทันตกรรม (Clinical skill Development in Dentistry)
การเรียนรู้การเคลื่อนไหวของร่างกายที่เกี่ยวข้องกับงานคลินิกทันตกรรม หลักการทำงาน ด้วยการรับรู้การเคลื่อนไหวของกล้ามเนื้อและข้อต่อ และประยุกต์สำหรับการปฏิบัติงานในทาง ทันตกรรม หลักการปฏิบัติงานด้านทันตกรรมที่สอดคล้องกับหลักการยะศาสตร์ การกำหนดท่าทาง และตำแหน่งในการทำงานที่สมดุล การจัดสภาพแวดล้อมในการทำงานที่ปลอดภัยและมี ประสิทธิภาพในการดูแลสุขภาพแก่ผู้ป่วย การใช้กระจกส่องปาก เครื่องดูดน้ำลายความแรงสูง หัวกรอความเร็วสูงและความเร็วต่ำอย่างมีประสิทธิภาพ ทักษะการใช้มือควบคู่กับการมองเห็นและดุลยภาพบำบัดเพื่อการป้องกันและแก้ไขการบาดเจ็บของระบบ กล้ามเนื้อ และกระดูกของร่างกาย
Learning of psychomotor skills in related to dental clinical practice, proprioceptive derivation principle and its application in dental clinical practice, application of ergonomics in dentistry, identification of balanced working posture & position, setting safe & healthy working environment to deliver effective health care, effective use of mouth mirror, hand and eye coordination skill; practice in appropriate working posture & position setting up dental instrument, equipment and working environment, handling of mouth mirror, high power suction, and instrument for tooth preparation, cooperated practice between dentist and assistant including Mind Body (Equilibrium). Therapy for prevention and correction of musculoskeletal injuries.
SCI02 1131 เคมีวิเคราะห์ 1 เทอม: 3-2567 จำนวน 3 หน่วยกิต
เวลา : วันจันทร์ 10:00-12:00น. ห้อง 1204, วันพุธ 11:00-12:00 น. ห้อง 1134
ผู้สอน: ผศ.ดร.ปิยะนุช, รศ.ดร.สัญชัย, รศ.ดร.กมลวัช และ ผศ.ดร.พัชรินทร์
|
เวลา |
หัวข้อ |
ผู้สอน |
|
|
24 และ 26 ก.พ. 3, 5, 10 มี.ค. 68 |
กระบวนการวิเคราะห์เชิงปริมาณ, ปริมาณสารสัมพันธ์เบื้องต้น, การวัดค่าและความคลาดเคลื่อนการใช้สถิติในการวิเคราะห์ข้อมูลทางเคมี, การวิเคราะห์โดยน้ำหนัก |
ผศ.ดร.ปิยะนุช ปิ่นอยู่ |
|
|
สอบย่อยครั้งที่ 1 |
|||
|
12, 17, 19, 24, 26, 31 มี.ค. 68 |
การวิเคราะห์ด้วยการไทเทรต สมดุลเคมีของปฏิกิริยาการตกตะกอน สมบัติของตะกอน ผลของสมดุลอื่นๆต่อสภาพละลายได้ของตะกอนการวิเคราะห์ด้วยการไทเทรตแบบตกตะกอน |
รศ.ดร.สัญชัย ประยูรโภคราช |
|
|
สอบกลางภาค: (11 เม.ย. 2568 เวลา 9:00-11:00 น.) |
|||
|
2, 21, 23, 27*, 28, 30 เม.ย. 68 (* ชดเชย 5 พ.ค. ฉัตรมงคล) |
สมดุลกรด-เบส โมโนโปรติกและพอลิโปรติก การไทเทรตกรด-เบสประเภทต่าง ๆ การใช้การไทเทรตกรด-เบสสำหรับการวิเคราะห์ปริมาณ สมดุลเคมีของปฏิกิริยาสารเชิงซ้อนการไทเทรตสารเชิงซ้อน เทคนิคการไทเทรตด้วย EDTA |
ผศ.ดร.พัชรินทร์ ชัยสุวรรณ |
|
|
สอบย่อยครั้งที่ 3 |
|||
|
7, 11*, 14, 19 และ 21 พ.ค. 68 (* ชดเชย 12 พ.ค. วันวิสาขบูชา)
|
เคมีไฟฟ้าพื้นฐาน และเทคนิคการวิเคราะห์แบบโพเทนชิโอเมตรี |
รศ.ดร.กมลวัช งามเชื้อ |
|
|
สอบประจำภาค (วันพุธที่ 28 พ.ค. 2568 เวลา 9:00-12:00 น.) |
|||
|
|
|
||
สัดส่วนการให้คะแนน
ตอนที่ 1 25%
ตอนที่ 2 25%
ตอนที่ 3 25%
ตอนที่ 4 25%
เอกสารอ้างอิง
- Skoog, D. A.; West, D. M.; Holler, F. J.; Crouch, S.R. Fundamentals of Analytical Chemistry, 8th ed., Thomson Learning: Belmont, 2004.
- Harris, D. C. Quantitative Chemical Analysis, 8th ed., W. H. Freeman: New York, 2010.
- Harvey, D. Modern Analytical Chemistry, McGraw-Hill: Boston, 2000.
This course covers most fundamental parts of calculus, which can be divided into two main parts – differentiation and integration. The course starts by giving a brief refresh of preliminary mathematical background which is necessary for learning and appreciating calculus. Then we go through the topics of limits and continuity, differentiation, applications of differentiation, integration, applications of the definite integral, and inverse functions.
SCI04 2011 Cell Biology 4(4-0-8)
วิชาบังคับก่อน: SCI04 1073 ชีววิทยา 2 และ SCI04 1074 ปฏิบัติการชีววิทยา 2
บทนำสู่วิชาชีววิทยาของเซลล์ องค์ประกอบทางเคมีของเซลล์ การได้มาและใช้พลังงานของเซลล์โพรแคริโอตและยูแคริโอต พลวัต โครงสร้างและหน้าที่ของส่วนประกอบในเซลล์และออร์แกเนลล์ ซึ่งได้แก่ เยื่อหุ้มเซลล์ นิวเคลียส ไมโทคอนเดรีย คลอโรพลาสต์ เพอร็อกซิโซม เอนโดพลาสมิกเรติคิวลัม พลวัต โครงสร้างและหน้าที่ของส่วนประกอบในเซลล์และออร์แกเนลล์ กอลจิแอพพาราทัส โครงร่างภายในเซลล์ เซลล์จังก์ชัน เซลล์แอดฮีชัน และเมทริกซ์นอกเซลล์ กลไกการสื่อสารภายในเซลล์ เทคนิคในการศึกษาเซลล์ เทคโนโลยีและนวัตกรรมด้านเซลล์ต้นกำเนิด เซลล์บาบัด และวิศวกรรมเนื้อเยื่อ
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้ที่คาดหวังระดับรายวิชา
นักศึกษาที่ผ่านรายวิชานี้มีความสามารถต่อไปนี้
1. อธิบายแนวคิดของนวัตกรรมที่เชื่อมโยงกับความรู้พื้นฐานทางชีววิทยาของเซลล์ (PLO3)
2. อธิบายหลักการเกี่ยวกับองค์ประกอบทางเคมี องค์ประกอบทางเคมีของเซลล์ การได้มาและใช้พลังงานของเซลล์โพรแคริโอตและยูแคริโอต พลวัต โครงสร้างและหน้าที่ของส่วนประกอบในเซลล์และออร์แกเนลล์ กลไกการสื่อสารภายในเซลล์ เทคนิคในการศึกษาเซลล์ เทคโนโลยีด้านเซลล์ต้นกำเนิด เซลล์บำบัด และวิศวกรรมเนื้อเยื่อ (PLO1)
3. เปรียบเทียบความเหมือนและแตกต่างของการได้มาและใช้พลังงาน โครงสร้างและหน้าที่ของส่วนประกอบในเซลล์และออร์แกเนลล์ ในเซลล์โพรแคริโอตและยูแคริโอต (PLO1)
4. สรุปความเชื่อมโยงของเมแทบอลิซึมของคาร์โบไฮเดรต โปรตีน ไขมัน และกรดนิวคลีอิค
5. ใช้ความรู้ทางชีววิทยาของเซลล์เพื่อตอบโจทย์ปัญหาที่กำหนดให้ (PLO1)
6. ใช้เทคโนโลยีสาระสนเทศในการสืบค้นเรื่องนวัตกรรมจากองค์ความรู้ด้านเซลล์ (PLO5)
7. สามารถนาเสนอข้อมูลแบบปากเปล่าโดยใช้สื่อพาวเวอร์พอยท์ และอภิปรายในชั้นเรียนในหัวข้อที่กำหนดให้โดยเคารพสิทธิและความคิดเห็นของผู้อื่น และส่งงานตามเวลาที่กำหนด (PLO 4 PLO6)
8. สามารถทำงานเป็นทีมเพื่อการนำเสนอและการดำเนินกิจกรรมการนำเสนอในชั้นเรียน (PLO7)
Prerequisite: SCI04 1073 Biology II and SCI04 1074 Biology Laboratory II
Introduction to cell biology, the chemical component of a cell, acquisition and use of cell energy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, dynamics, structure and functions of cellular components and organelles which includes cell membrane, nucleus, mitochondria, chloroplast, peroxisomes, the endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus, cytoskeleton, cell junctions, cell adhesion, and extracellular matrix, mechanisms of cell communication, techniques for studying cell, and technologies and innovations in stem cell, cell therapy, and tissue engineering.
Expected learning outcomes:
Upon completion of this course, students will be able to:
1. Describe the concepts of innovations and products connected to the fundamentals of cell biology (PLO3);
2. Explain the principles of chemical component of a cell, acquisition and use of cell energy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, dynamics, structure and functions of cellular components and organelles, mechanisms of cell communication, techniques to study cells, stem cell technology, cell therapy, and tissue engineering (PLO1);
3. Compare the similarity and difference of the acquisition and use of cell energy of prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells (PLO1);
4. Summarize the connected metabolisms of carbohydrates, proteins, lipids, and nucleic acids (PLO1);
5. Use the knowledge of cell biology to answer the given questions (PLO1);
6. Use information technology to search for the innovations and products based on the cell biology knowledge (PLO5);
7. Orally present the information in the given topic with a use of PowerPoint and give a class discussion with the respect to rights and opinions of others and submit work assignments on time (PLO4, PLO6);
8. Work as a team for presenting and managing the class presentation activity (PLO7).
SCI04 6401 Cell Biology 3(3-0-6)
Prerequisite: None
Biological studies at the cellular level, including biomolecules of cell composition, structures and functions of organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, cellular matrix, cytoskeleton, chloroplast, mitochondria, and nucleus), cell junctions, cell motility, metabolism and bioenergy transformation in cells, DNA-replication, transcription, translation, cell cycle and controls, cell division, and basic techniques to study cells.
Learning Outcomes
Expected Learning Outcomes:
On completion of this course, students are able to:
- Explain principles of biomolecules of cell composition, structures and functions of organelles (cell membrane, cell wall, cellular matrix, cytoskeleton, chloroplast, mitochondria, and nucleus), cell junctions, cell motility, metabolism and bioenergy transformation, DNA-replication, transcription, translation, cell cycle and controls, cell division, and basic techniques to study cells;
- Self-study via different learning sources on the current techniques to study cells for presenting and discussing with others in the classroom;
- Apply the learning knowledge to solve the given problems in environmental cell biology.
104863 Silver Nanoparticles and Bio-applications
Prerequisite: None
Principles of silver nanoparticle synthesis via chemical, physical and biological approaches, morphology, properties, and mechanisms of anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-viral, anti-inflammation, anti-angiogenic, and anti-cancer activities, applications as antibacterial agents and sensors for detecting biomolecules and metal ions, and current topics of bio-applications of silver nanoparticles.
Expected Learning Outcomes:
On completion of this course, students are able to:
1. Explain principles of silver nanoparticle synthesis via chemical, physical and biological approaches, morphology, properties, and mechanisms of anti-bacterial, anti-fungal, anti-viral, anti-inflammation, anti-angiogenic, and anti-cancer activities, applications as antibacterial agents and sensors for detecting biomolecules and metal ions;
2. Self-study on current topics on the bio-applications of silver nanoparticles via different learning sources, including information technology, to present and discuss with others in the classroom;
3. Apply the learning knowledge to solve the given problems on silver nanoparticles for bio-applications.
คำอธิบายรายวิชา (Course Description)
กฎการเคลื่อนที่ของนิวตัน การเคลื่อนที่แบบเชิงเส้นและแบบหมุน โมเมนตัมเชิงเส้น โมเมนตัมเชิงมุม พลังงานกล ทฤษฏีบท งานพลังงาน การเคลื่อนที่แบบซิมเปิลฮาร์มอนิก การแกว่งกวัดแบบหน่วงและเรโซแนนซ์ การแผ่ของคลื่น คลื่นเสียง การไหลของของไหล
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้รายวิชา (Course Learning Outcomes)
- บอกความหมายและคำนวณปริมาณทางกายภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเคลื่อนที่ใน 1 และ 2 มิติได้
- คำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเคลื่อนที่แบบต่างๆ ได้ด้วยการประยุกต์กฏการเคลื่อนที่ของนิวตัน
- คำนวณปริมาณ งาน พลังงาน ระบุสถานการณ์ และ ประยุกต์ทฤษฎีบทงานพลังงานและหลักการอนุรักษ์พลังงานได้
- คำนวณปริมาณ โมเมนตัม การดล และระบุสถานการณ์ที่มีโมเมนตัมคงตัวได้
- บอกความหมายและคำนวณปริมาณทางกายภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการหมุนของวัตถุแข็งเกร็ง คำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวกับการหมุนด้วยการประยุกต์กฏการเคลื่อนที่ของนิวตัน คำนวณปริมาณโมเมนตัมเชิงมุมของวัตถุและ ระบุสถานการณ์ที่มีโมเมนตัมเชิงมุมคงตัวได้
- คำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการกวัดแกว่งฮาร์มอนิก บอกชนิดของการกวัดแกว่งแบบหน่วง บอกความถี่เรโซแนนซ์ของระบบได้
- บอกความหมายและคำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวข้องกับคลื่นกล การแผ่คลื่น และคลื่นนิ่งในตัวกลางได้
- บอกความหมายของและคำนวณปริมาณแรงทางกายภาพในระบบของไหล ประยุกต์สมการความต่อเนื่องและสมการเบอร์นูลีในการหาค่าความดันและอัตราเร็วของของไหลในอุดมคติได้

-
คำอธิบายรายวิชา (Course Description)
กฎการเคลื่อนที่ของนิวตัน การเคลื่อนที่แบบเชิงเส้นและแบบหมุน โมเมนตัมเชิงเส้น โมเมนตัมเชิงมุม พลังงานกล ทฤษฏีบท งานพลังงาน การเคลื่อนที่แบบซิมเปิลฮาร์มอนิก การแกว่งกวัดแบบหน่วงและเรโซแนนซ์ การแผ่ของคลื่น คลื่นเสียง การไหลของของไหล
-
ผลลัพธ์การเรียนรู้รายวิชา (Course Learning Outcomes)
- บอกความหมายและคำนวณปริมาณทางกายภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเคลื่อนที่ใน 1 และ 2 มิติได้
- คำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการเคลื่อนที่แบบต่างๆ ได้ด้วยการประยุกต์กฏการเคลื่อนที่ของนิวตัน
- คำนวณปริมาณ งาน พลังงาน ระบุสถานการณ์ และ ประยุกต์ทฤษฎีบทงานพลังงานและหลักการอนุรักษ์พลังงานได้
- คำนวณปริมาณ โมเมนตัม การดล และระบุสถานการณ์ที่มีโมเมนตัมคงตัวได้
- บอกความหมายและคำนวณปริมาณทางกายภาพที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการหมุนของวัตถุแข็งเกร็ง คำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวกับการหมุนด้วยการประยุกต์กฏการเคลื่อนที่ของนิวตัน คำนวณปริมาณโมเมนตัมเชิงมุมของวัตถุและ ระบุสถานการณ์ที่มีโมเมนตัมเชิงมุมคงตัวได้
- คำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวข้องกับการกวัดแกว่งฮาร์มอนิก บอกชนิดของการกวัดแกว่งแบบหน่วง บอกความถี่เรโซแนนซ์ของระบบได้
- บอกความหมายและคำนวณปริมาณที่เกี่ยวข้องกับคลื่นกล การแผ่คลื่น และคลื่นนิ่งในตัวกลางได้
- บอกความหมายของและคำนวณปริมาณแรงทางกายภาพในระบบของไหล ประยุกต์สมการความต่อเนื่องและสมการเบอร์นูลีในการหาค่าความดันและอัตราเร็วของของไหลในอุดมคติได้